Fiat vs Crypto: Differences between fiat currency and cryptocurrency
Discover the key differences between fiat currency and cryptocurrency, their advantages, challenges, and how they're shaping the future of money.
By Corey Barchat
Money is evolving at a rapid pace. From bartering goods to using physical coins and paper bills, it has gradually transformed over time into a vast digital ecosystem.
While fiat currency is still the standard for modern trade and commerce, cryptocurrency has emerged as a challenge to the dominance of government-issued fiat money like the US dollar and euro. Since the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, users have been presented with an alternative that offers decentralization, lower fees, and greater financial autonomy.
This ongoing debate—fiat vs. crypto—has sparked discussions among economists, technologists, and consumers. But is one better than the other?
This article explores the differences between fiat currency and cryptocurrency, their respective advantages, and the challenges they present.
Fiat vs. Crypto: Key differences
While fiat currency is centralized, controlled by governments and banks, and prone to inflation, cryptocurrencies like BTC are decentralized with fixed supplies. Fiat money is universally accepted but less private, whereas cryptocurrencies offer greater privacy but face higher volatility and regulatory uncertainty.
In short, fiat currency and cryptocurrency differ significantly in their structures, governance, and operational principles. Here are some of the main difference areas:
Centralization vs. decentralization
Control and governance
Fiat currencies are controlled by central authorities like governments and central banks, which set monetary policies to manage inflation, interest rates, and the money supply. Central banks (like the Federal Reserve in the United States) use these tools to influence economic stability, but this also means that the government has significant control over the economy.
Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, operate on decentralized networks built on blockchain technology. Control is distributed across the blockchain, preventing any single entity from manipulating the currency. Governance instead relies on consensus algorithms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS), which secure the network and ensure that protocol changes are democratically approved by a majority of participants.
Trust vs trustless systems
Fiat money operates on a system of trust in government institutions, where citizens believe in the authority and stability of the issuing body. However, trust can sometimes waver in times of political or economic instability, leading to financial crises and hyperinflation.
Cryptocurrencies, by contrast, operate on trust in cryptographic code and mathematical algorithms, rather than in people or institutions. Trust in these systems comes from the transparency and immutability of the blockchain, which guarantees that transactions are secure and tamper-proof, even in the absence of a central authority.
Inflation vs. deflation
Fiat inflationary pressures
Fiat currencies are susceptible to inflation, especially when governments print too much currency and increase the money supply. If done incorrectly, this can erode purchasing power, leading to rising prices for goods and services over time. While central banks attempt to control inflation through monetary policy, poor decisions or economic shocks can result in hyperinflation.
Deflationary crypto assets
While some cryptocurrencies may not have a fixed supply, Bitcoin is designed to be deflationary due to its limited supply. In fact, only 21 million Bitcoins will ever exist, making it impossible to "print" more. This scarcity can drive up the value of the currency over time, but "HODLing" can also lead to hoarding, reducing liquidity in cryptocurrency markets and making BTC less practical as a medium of exchange.
Transaction speed and costs
Fiat transaction fees
Fiat money transactions, especially in modern banking, can be processed instantly via digital payment systems and fiat wallets. However, international transfers and cross-border payments can take days to settle due to intermediary banks and complex financial networks.
Fiat transfers can also incur high fees, especially for global transactions, currency exchanges, and credit card processing. These fees have a wide range, from small percentages to significant amounts, depending on the intermediary.
Instant crypto transactions
Cryptocurrency transactions, particularly on blockchain networks like Bitcoin, can also be processed relatively quickly, but network congestion can lead to delays. Newer blockchain platforms, such as Ethereum 2.0 (Post-Merge Ethereum) and Solana, are designed to process transactions faster, though they still depend on network conditions.
Users may choose to transact in crypto due its lower fees, especially when sending large sums of money at once. However, during periods of high demand, transaction fees can spike, particularly on networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum. To combat this, there are alternative tokens (altcoins) designed with scalability and lower fees in mind, such as Litecoin and XRP.
Privacy and anonymity
Cryptocurrency transparency
Cryptocurrencies are built on blockchain technology, which means that every transaction is recorded and verified on a public ledger. While the identities or individuals behind wallet addresses are not immediately visible, advanced tracing techniques (such as dusting attacks) can sometimes de-anonymize users. This transparency is a double-edged sword: it ensures accountability but also raises concerns about privacy.
Fiat money privacy
Fiat currency transactions, particularly digital ones, are closely monitored by financial institutions and governments. While cash offers users a degree of anonymity, most digital fiat transactions are subject to surveillance. Governments and banks can freeze accounts, track spending patterns, and impose sanctions, which may raise concerns about privacy for individuals seeking greater financial independence.
Accessibility and usability
Global accessibility
Fiat currencies are widely accepted across the global financial system. However, access to traditional banking systems can be limited in certain regions, especially in developing countries. Many people remain unbanked or underbanked, relying on informal financial systems and international remittances from friends and family.
Enter crypto.
In contrast, cryptocurrencies offer global accessibility to anyone with an internet connection, providing an alternative for those excluded from traditional financial systems. However, cryptocurrencies are still not universally accepted, and access can be limited in countries with restrictive regulations.
Everyday transactions
Fiat money is incredibly easy to use for everyday transactions. From buying groceries in-person to paying bills online, fiat is the go-to currency due to its widespread acceptance and established infrastructure.
Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, are not as practical for everyday use. It's true that the technology is constantly improving and growing number of merchants are beginning to accept crypto payments. However, the learning curve and volatility of cryptocurrency prices still present barriers that make it less convenient for everyday transactions.
Aspect | Fiat Money | Cryptocurrencies |
Control | Centralized (governments and central banks) | Decentralized (blockchain networks) |
Inflation | Prone to inflation due to government policies | Fixed supply in many cases (e.g., Bitcoin) |
Transaction Speed | Fast domestically, slow internationally | Varies by blockchain, often faster |
Fees | High for international transfers | Low, but can vary during network congestion |
Privacy | Low privacy, subject to government oversight | High potential privacy, but transactions are transparent |
Accessibility | Widely accepted but limited in some regions | Accessible globally with an internet connection |
Ease of Use | Simple and widespread | Growing but not yet universally accepted |
Advantages of fiat money
Fiat currency has long been the cornerstone of global economies, offering a stable and widely-accepted medium of exchange. Here are some of its key benefits:
Stability and acceptance
Fiat money enjoys universal acceptance across nearly all countries. Whether you’re shopping at a local grocery store or traveling abroad, fiat currencies are the default means of exchange. The government backing of this currency means that people (and businesses) are willing to accept fiat in exchange for goods and services.
Compared to cryptocurrencies, fiat money is relatively stable. While inflation can reduce its purchasing power in certain circumstances, fiat currencies do not experience the same extreme volatility as cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. This helps to make them more reliable for purposes like daily transactions and savings.
Regulatory oversight
One of the strengths of fiat money is the regulatory framework surrounding it. Governments implement consumer protections via laws and anti-fraud measures to ensure safe and secure transactions. Having centralized oversight can make it easier to prevent and recover from fraud, offering consumers a level of security that cryptocurrencies may not provide.
In addition to federal government, central banks play a crucial role in managing national economies. Adjusting interest rates and controlling the money supply via monetary policy are some of the levers available for central banks to respond to economic crises, stabilize inflation, and promote growth. Such levels of control are simply not possible (or even intended) in decentralized cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Integration with existing financial systems
Fiat money can be fully integrated with the existing banking infrastructure of a country or region. From checking accounts to credit cards to fiat wallets, fiat money powers the financial products and services that billions of people around the world rely on daily. This established network naturally makes fiat the default choice for the majority of financial transactions.
Some common use cases of fiat currencies include the creation of complex financial products like loans, mortgages, insurance, and other investment vehicles. These products are not yet widely available in the cryptocurrency space—with some exceptions—making fiat the go-to for personal and business finance on a global scale.
Advantage | Fiat Currency |
Stability | Fiat currencies are relatively stable, especially in well-regulated economies. |
Universal Acceptance | Widely accepted for trade and commerce globally, making it easy to use anywhere. |
Regulatory Oversight | Central banks and governments provide strong oversight and consumer protections. |
Integration with Financial Systems | Fully integrated with traditional banking and financial systems. |
Use in Financial Products | Essential for loans, mortgages, and other complex financial products. |
Advantages of cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies bring a revolutionary approach to finance, presenting a decentralized alternative to the traditional financial system:
Decentralization and autonomy
One of the key advantages of cryptocurrencies is their freedom from centralized control. Decentralized cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin operate without interference from central banks or governments, giving users financial autonomy and censorship resistance.
Peer-to-peer crypto transactions provide some added benefits, like lower fees, faster payment speed, greater control over their funds. Cryptocurrency also opens up possibilities for cross-border payments without the complexities, delays, and fees of international banking systems.
Security and transparency
There are key aspects of blockchain technology that make cryptocurrency transactions secure. For instance, the decentralized nature of blockchain, combined with advanced cryptographic techniques, make it nearly impossible to alter or tamper with transaction records.
The openness of blockchain ledgers allows anyone—whether they've used the blockchain or not—to verify transactions themselves. This helps reduces the need for third-party trust and the potential for fraud, since trust is distributed across the decentralized network.
Innovation and future potential
In recent years, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) have worked to position themselves at the forefront of financial innovation. Blockchain is driving the development of decentralized finance (DeFi), tokenized assets, and new ways of managing digital ownership and identity.
Ethereum DeFi applications (dApps) alone have created billions of dollars in total value locked (TVL), presenting new opportunities for lending, borrowing, and investing without intermediaries. However, users should be aware of the unique risks that accompany participating in DeFi. And in traditional finance, the approval of Bitcoin Spot ETFs (and their Ethereum counterpart) has paved the way for greater mainstream adoption and governmental acceptance.
Additionally, while use cases are still limited, blockchain technology is being explored for applications beyond finance, such as supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems.
Advantage | Cryptocurrency |
Decentralization | Cryptocurrencies operate independently of governments, offering financial autonomy. |
Lower Transaction Costs | Peer-to-peer transactions often come with lower fees, especially for large amounts. |
Security | Blockchain technology provides robust security, making transactions nearly tamper-proof. |
Transparency | All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud. |
Innovation and Future Potential | Promotes financial innovation through decentralized finance (DeFi) and other blockchain applications. |
Challenges of fiat currency and cryptocurrency
While both fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies present unique advantages, they are not without their drawbacks:
Volatility and speculation
Most fiat currencies are generally stable, with central banks working to minimize inflation and maintain economic stability in their respective countries. In contrast, cryptocurrencies are highly volatile assets with little intrinsic value.
Crypto price stability can fluctuate dramatically within short periods, driven by factors like market sentiment, news, and speculation. While this volatility can create opportunities for profit, it also introduces significant risks for investors and everyday users.
Regulatory and legal issues
Fiat money is recognized as legal tender, meaning it must be accepted for payments by law in a given country. Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, do not have the same legal status, and face regulatory scrutiny across the globe.
While some businesses accept crypto payments, governmental and regulatory bodies are still grappling with how to classify and regulate digital currencies, which generally lack legal tender status. This has led to a patchwork of laws and regulations in different regions that can stifle innovation and limit adoption of digital assets.
Environmental concerns
Cryptocurrency mining, particularly for Proof-of-Work (PoW) tokens, consumes enormous amounts of electricity. For example, Bitcoin alone consumes more electricity than a country the size of Poland. While some blockchains like Ethereum have moved to the more efficient Proof-of-Stake (PoS), crypto mining still represents a significant concern, leading to discussions about the long-term sustainability of cryptocurrencies.
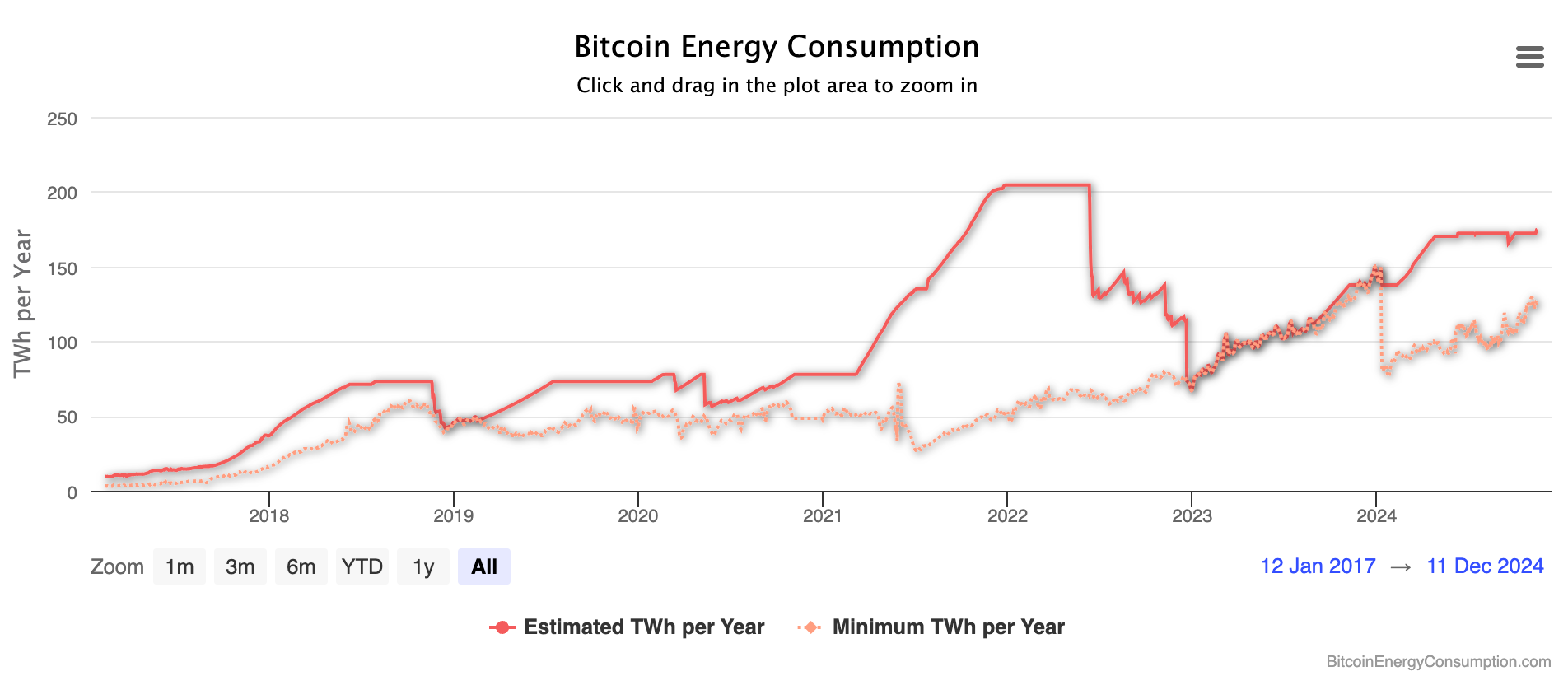
While cryptocurrencies have come under fire for their environmental impact, traditional fiat systems also have environmental costs. Printing money, maintaining physical bank branches, and running centralized financial systems all consume resources, though they are generally considered less energy-intensive than cryptocurrency mining.
Bridging the gap between fiat and crypto
As the world increasingly embraces both fiat currency and cryptocurrencies, users need options to move seamlessly between the two.
MoonPay offers an easy and fast way to bridge the gap, enabling users to buy, sell, and manage cryptocurrencies with fiat money.
To begin, top up your wallet in euros, pounds, or dollars and use your MoonPay Balance to buy crypto like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH). Once funded, use your balance for faster, cheaper transactions and higher approval rates. When you're ready to withdraw, enjoy zero-fee transfers straight to your bank account.
Whether you’re looking to explore digital currencies for the first time or need a reliable platform for everyday transactions, MoonPay Balances is here to help.

.png)


.png)