What are Spot Bitcoin ETFs and how do they work?
Discover what Bitcoin Spot ETFs are and how they work to combine traditional financial instruments with cryptocurrency investing.
By Corey Barchat

Disclaimer: The following is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as financial or investment advice.
Bitcoin is the first and most prominent cryptocurrency, worth fractions of a cent when it debuted in 2009.
Since then, it has grown to possess a market cap above $1 trillion, attracting increased attention around the globe.
While accessing Bitcoin (BTC) may be intuitive for some, not everyone is willing to manage a crypto wallet, private keys, and the responsibility of "HODLing" BTC. So as demand for Bitcoin investments has grown, financial instruments like Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have emerged to facilitate broader market access.
In this article, we explore Spot Bitcoin ETFs, their structure, functionality, advantages, risks, and the regulatory landscape surrounding them.
What is a Spot Bitcoin ETF?
A Spot Bitcoin ETF is an exchange-traded fund designed to track the market price of Bitcoin directly. Unlike Bitcoin futures-based ETFs, Spot Bitcoin ETFs hold actual Bitcoin in their portfolios, allowing investors to gain exposure to Bitcoin without managing the cryptocurrency themselves.

Another type of exchange-traded funds is Bitcoin futures ETFs. These focus on tracking the price of Bitcoin futures contracts, which are agreements to buy or sell Bitcoin at a predetermined price on a future date.
In contrast, a Spot Bitcoin ETF holds Bitcoin directly, providing a straightforward and direct connection to the spot price of Bitcoin. This direct exposure allows Spot Bitcoin ETFs to closely mirror Bitcoin's market value, making them an option for investors seeking a traditional ETF structure with exposure to cryptocurrency.
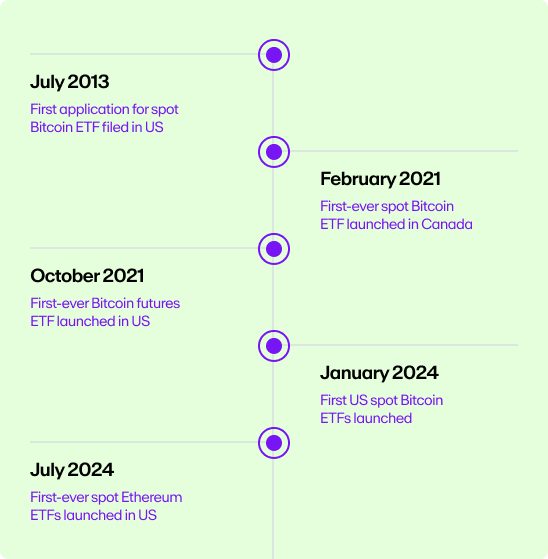
History of Bitcoin ETFs
The journey to establish Spot Bitcoin ETFs has been marked by regulatory proposals and market evolution, both in the United States and Canada.
Here are some significant milestones along the way:
2013 - First Bitcoin ETF Proposal in the U.S.
2017 - CME and CBOE Launch Bitcoin Futures in the U.S.
2018 - U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Rejects Bitcoin ETF Proposals
2021 - First Spot Bitcoin ETF in Canada

2021 - First SEC-Approved Bitcoin Futures ETF
2022 - New U.S. Bitcoin Futures ETF Launches
2022 - SEC Rejects Additional Spot Bitcoin ETF Proposals
2023 - Spot Bitcoin ETFs Launch in Other Countries
2023 - Bitcoin Spot ETF Proposals Gain Traction in the US
2024 - SEC Approves Spot Bitcoin ETF Trading in the US
2024 - SEC Approves Ethereum ETF Trading in the US
How do Spot Bitcoin ETFs work?
Spot Bitcoin ETFs generally work by directly holding Bitcoin as the underlying asset and issuing shares that represent proportional ownership in the ETF’s Bitcoin holdings. This setup allows investors to trade shares of the ETF on a stock exchange, similar to traditional ETFs.
ETF structure and operation
A Spot Bitcoin ETF typically involves a fund sponsor or issuer responsible for managing the ETF's operations. This includes buying, selling, and holding Bitcoin.

Bitcoin ETFs issue shares to investors who can trade them on major stock exchanges. The share price generally reflects the current value of the underlying Bitcoin assets, adjusted for fees and expenses.
Custody and storage of BTC assets
Spot Bitcoin ETFs require robust custody solutions to store their Bitcoin holdings. They often work with custodians specializing in cryptocurrency storage.
These custodians employ various security measures, such as cold storage (offline wallets), multi-signature protocols, and insurance policies to custody the Bitcoin assets.
However, even with security measures in place, there are still potential risks involved with custodians storing large quantities of Bitcoin, which we will see later.
Creation and redemption
Spot Bitcoin ETFs operate through a creation and redemption mechanism. Authorized participants (APs), typically large financial institutions, can create or redeem ETF shares by transacting with the underlying Bitcoin.
When creating shares, APs deliver Bitcoin to the ETF in exchange for newly issued shares. For redemption, APs return shares to the ETF in exchange for the equivalent amount of Bitcoin.
It's important to note that, unlike some traditional ETFs, Spot Bitcoin ETFs do not pay dividends. This is because underlying bitcoins do not generate income. Instead, investors can only benefit from the potential appreciation in the price of BTC.
Other Bitcoin investment vehicles
Bitcoin Futures-Based ETFs
Bitcoin futures-based ETFs track the price of Bitcoin futures contracts, which are agreements to buy or sell Bitcoin at a future date.

These ETFs can offer exposure to Bitcoin price trends, but they may experience tracking errors due to the complexity of futures markets.
Bitcoin Mutual Funds and Trusts
Bitcoin mutual funds and trusts, like the Grayscale Bitcoin Trust, hold Bitcoin on behalf of investors.
These vehicles typically trade at a premium or discount relative to the underlying Bitcoin, which can lead to price discrepancies.
Bitcoin Derivatives
Bitcoin derivatives and options allow investors to speculate on Bitcoin price movements without owning the underlying asset.
While these instruments offer flexibility and potential leverage, they carry significant risk of loss due to their complex nature.
Aspect | Spot Bitcoin ETFs | Bitcoin Futures-Based ETFs | Bitcoin Mutual Funds | Bitcoin Derivatives |
Definition | ETFs that hold and track the spot price of Bitcoin. | ETFs that invest in Bitcoin futures contracts. | Mutual funds that invest in Bitcoin or related assets. | Financial contracts derived from Bitcoin (options, futures, etc.). |
Underlying Asset | Bitcoin. | Bitcoin futures contracts. | Bitcoin or related assets. | No direct Bitcoin ownership; linked to futures or options. |
Price Correlation | Directly correlates to Bitcoin's spot price. | Correlates to the price of futures; could differ from spot prices. | Can correlate to Bitcoin but might include additional assets. | Variable, depending on contract structure. |
Risks | Volatility, custody issues, regulatory uncertainty. | Tracking errors, market roll risks, volatility. | Can trade at a premium/discount; volatility risks. | High risk due to leverage, complexity, and market fluctuations. |
Limitations | Custody risks, regulatory delays, price volatility. | Tracking errors, higher fees due to futures market structure. | Potentially limited liquidity; possible premiums/discounts. | High risk due to leverage, complex contract structures. |
Characteristics of Bitcoin ETFs
Spot Bitcoin ETFs have several unique characteristics that are worth highlighting.
Accessibility for mainstream investors
Spot Bitcoin ETFs provide a familiar investment vehicle for mainstream investors, allowing them to access Bitcoin through traditional brokerage accounts. This accessibility lowers barriers to entry, potentially broadening the investor base.
Exposure to Bitcoin price movements
Investors in Spot Bitcoin ETFs gain exposure to the price of Bitcoin without owning or managing the underlying asset. This approach offers a way to participate in the cryptocurrency market without the complexities of wallet management or private keys.
Portfolio diversification
Spot Bitcoin ETFs could add diversification to investment portfolios. Bitcoin's price movements often differ from traditional assets, providing potential diversification and reducing overall portfolio risk.
Did you know? Another potential way to manage risk is through dollar-cost averaging (DCA)
Efficiency
Spot Bitcoin ETFs offer a convenient and efficient way to invest in Bitcoin, without some of the negative environmental side effects of Bitcoin mining. Investors can buy and sell ETF shares on the stock exchange, rather than using cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets.
Risks of Bitcoin ETFs
Spot Bitcoin ETFs also come with potential limitations, challenges, and risks.
Market volatility and Price Fluctuations
Bitcoin's price is notoriously volatile, leading to significant fluctuations in the value of Spot Bitcoin ETFs. Investors should be prepared for sudden price changes and potential market downturns that could significantly impact their holdings.
Counterparty risks
Spot Bitcoin ETFs rely on custodians to store their Bitcoin assets securely. Counterparty risks arise if custodians fail to maintain proper security or face operational issues, potentially impacting the ETF's performance and investor confidence.
Custodial security risks
In addition to counterparty issues, the custodian managing Bitcoin for Spot Bitcoin ETFs must ensure robust security to prevent theft or unauthorized access. Despite best efforts, the risk of security breaches remains a concern, and custodial issues can affect the ETF's integrity.
Did you know? Crypto security is vital for everyone, not just for ETF custodians. Read our helpful guides to learn about private keys, wallet addresses, as well as best security practices and how to avoid crypto scams.
Regulatory uncertainty
The regulatory landscapes for Spot Bitcoin ETFs and the underlying Bitcoin are evolving, leading to uncertainty and legal risks. Changes in regulations or government policies can impact the legality and operation of ETFs, while affecting investor sentiment.
Additional risks
Beyond the main risks, Bitcoin ETFs also carry some additional challenges:
- Tracking errors can occur due to market disruptions or discrepancies between ETF share prices and Bitcoin's spot price.
- Liquidity risks may arise during periods of market stress, potentially impacting share trading.
- Operational complexities in managing Bitcoin assets can lead to further challenges in ETF management.
Spot Bitcoin ETF Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Do Bitcoin Spot ETFs use custodians
Bitcoin Spot ETFs use custodians to store their Bitcoin assets. These custodians typically employ security measures, such as hardware wallets, multi-signature protocols, and insurance policies, to help minimize the risk of theft or unauthorized access.
What fees are associated with Bitcoin Spot ETFs?
Bitcoin Spot ETFs generally have management fees, similar to traditional ETFs. These fees cover the costs of managing the fund, including custody, storage, and regulatory compliance. Be sure to review the expense ratio and other associated costs before investing in Spot Bitcoin ETFs.
What was the first Spot Bitcoin ETF?
Bitcoin Spot ETFs were first approved and introduced in Canada in early 2021. Since then, several other countries have followed suit, with various jurisdictions granting approval for Spot Bitcoin ETFs. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission approved trading Spot Bitcoin ETFs in January 2024.
What is the difference between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Spot ETF?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency that users can manage through custodial and non-custodial wallets. A Bitcoin Spot ETF, on the other hand, is an investment vehicle that directly holds Bitcoin and trades on traditional stock exchanges.
Are there other cryptocurrency ETFs?
As of 2024, crypto ETFs aren’t just limited to Bitcoin. Ethereum ETFs have recently secured approval, allowing retail investors to gain exposure to Ethereum in much the same way that they can with a Bitcoin ETF.
Gain exposure to Bitcoin
If Spot Bitcoin ETFs aren’t right for you, there are other ways to gain Bitcoin exposure.
MoonPay makes it easy to buy Bitcoin (BTC) and other crypto assets using a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods. Just enter the amount of BTC you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order.
Where to sell Bitcoin
MoonPay also makes it easy to sell Bitcoin when you decide it's time to cash out. Simply enter the amount of BTC you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.






.png)