What is a wallet address? A guide to crypto wallet addresses
Learn what crypto wallet addresses are, what differentiates them, and how you can practice crypto wallet safety techniques when dealing with digital assets.
By Corey Barchat

One of the most important fundamentals when it comes to cryptocurrency and Web3 is the crypto wallet.
Without them, everyone would lack the means to store, send, and receive digital assets in a secure manner. But even cryptocurrency wallets themselves would be incomplete without a wallet address.
So what is this unique identifier that distinguishes each wallet, and allows anyone to send cryptocurrency across the globe?
This guide aims to demystify wallet addresses, explain how they work, their different types, and security techniques to help keep your crypto safe.
What is a wallet address?
A wallet address is a unique string of characters that serves as a destination for sending and receiving cryptocurrency. Much like a traditional bank account number, a wallet address is your unique identifier that allows you to manage your assets securely.
However, unlike a bank account, which typically has your name associated with it, a cryptocurrency wallet address is pseudonymous, meaning it does not directly reveal your identity.
These addresses are alphanumeric, usually a lengthy string of letters and numbers, and are specific to each type of cryptocurrency. For instance, the structure of a Bitcoin wallet address will differ from an Ethereum wallet address.
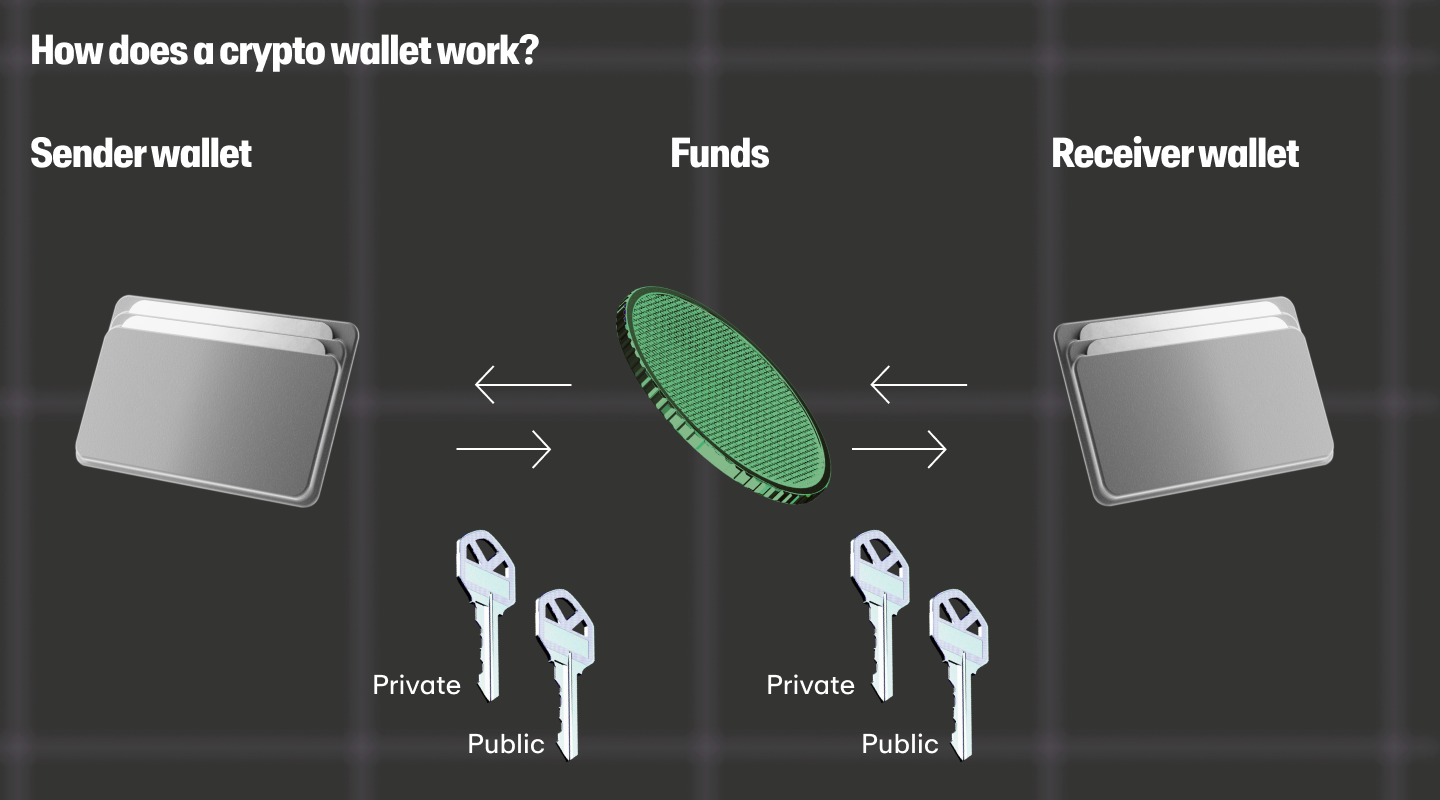
How does a crypto wallet address work?
When you initiate a cryptocurrency transaction, whether it's sending or receiving funds, the process relies heavily on wallet addresses. Here's a simplified breakdown of how it works:
1) Generating the wallet address
When you create a cryptocurrency wallet, the software or platform generates a unique address for you. This address is essentially the digital equivalent of your physical mailbox.
If you can't remember the entire string of numbers and letters, don't worry. Most wallet applications allow you to copy your wallet address when sending or receiving cryptocurrency.
2) Sending cryptocurrency
If you want to send cryptocurrency to someone else, you'll need to know their crypto wallet address. Any time that you send crypto, you will have to input their exact address into your wallet software along with the amount you wish to send. The send transaction is then broadcasted to the blockchain network for confirmation.
3) Verifying transactions
Each transaction is verified by the network of computers (nodes) using cryptographic techniques. Once verified, it's added to a "block" and appended to the blockchain, which serves as a public ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions.
4) Receiving cryptocurrency
When someone sends you cryptocurrency, they'll need to input your public wallet address into their own wallet application. The cryptocurrency is then sent from their wallet to yours.
How do I find my wallet address?
If you can't remember the entire string of numbers and letters, don't worry. Just follow these steps to find your wallet address:
- Open your crypto wallet app or software.
- Navigate to the "Receive" or "Deposit" section.
- Your wallet address will be displayed here.
Most crypto wallets allow you to copy the entire address directly, and may also provide a QR code for easy sharing. However, it's still important to double check the full wallet address or carefully scan the QR code to avoid errors when receiving funds.
What are the different types of crypto wallet addresses?
There are various types of cryptocurrency wallet addresses, each associated with different cryptocurrencies and blockchain networks. Here are a few examples:
Bitcoin wallet addresses
Bitcoin addresses typically start with either '1', '3', or 'bc1'. The diversity arises from different wallet address formats, with each serving specific purposes. For example, '1' Bitcoin addresses are for standard transactions, '3' for multi-signature transactions, and 'bc1' for Segregated Witness transactions.
Bitcoin wallet address examples
- Bitcoin address (Legacy): 1B7S72VF27rkFtra8GZgCn1RJNhE2su6rY
- Bitcoin address (SegWit): bc1qf2kdgu2vlctqlnlxk4smkxd68grl5q2we8dzfd
Ethereum wallet addresses
Ethereum addresses too consist of numbers and letters, however they are longer than Bitcoin addresses and always begin with '0x'. Ethereum addresses are used for transactions involving Ether (ETH) and other ERC-20 tokens (including Ethereum NFTs).
Ethereum wallet address examples
- Ethereum address 1: 0xAcF36260817d1c78C471406BdE482177a1935071
- Ethereum address 2: 0x87D487fa59274545743949BE4282EA87F316821E
Other blockchain-specific addresses
Every blockchain has their own unique wallet address format. For example, Litecoin addresses start with 'L' or 'M', while Ripple (XRP) addresses begin with 'r'. Both consist of a combination of letters and numbers as well.
Other blockchain wallet address examples
- Litecoin (LTC) address: LSWDynyeNPevqnERfLBZPUpLMaVibo85i2
- Ripple (XRP) address: raNoQsByFJYmzaAvs5FFGcB4q5bvpbDfqh
Understanding the specific format for each blockchain is important to avoiding errors in crypto transactions. For instance, some digital wallets may support multiple address formats, but using the correct format is always key.
If you erroneously send crypto to the wrong wallet address, there will be no way to recover the cryptocurrency. For example, sending Bitcoin to an Ethereum blockchain address or vice versa will result in the loss of funds.
Why are wallet addresses important?
Understanding the importance of wallet addresses goes beyond the basic mechanics of cryptocurrency transactions. Here are some key aspects:
Unique identifier
A wallet address serves as a unique identifier for crypto transactions, similar to an account number in traditional banking. It is key to sending and receiving cryptocurrencies on the blockchain, ensuring that transactions are routed to the correct recipient.
Crypto safety
Wallet addresses play a pivotal role in ensuring the security of your cryptocurrencies. By safeguarding your private keys and sharing only your public address, you can help mitigate the risk of unauthorized access to your cryptocurrency.
Storing digital assets
Your wallet address is the gateway to storing and managing your crypto assets. Whether you're HODLing Bitcoin for investment or participating in decentralized finance (DeFi) on the Ethereum network, your crypto wallet address is the key to accessing and controlling your funds.
Free to download
Most crypto software wallets are free to download and use. So whether you opt for a hardware wallet*, software wallet, or a mobile wallet, having a wallet address grants you access to the world of cryptocurrencies without incurring additional costs.

*Note: hardware wallets generally are not free, as you'll need to order the physical equipment used for cold storage.
New potential for Web3 transactions
As the crypto space evolves, the integration of Web3 technologies introduces new possibilities for decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Your wallet address becomes not just a receiver of funds but a gateway to engaging with the decentralized internet.
Safety tips for managing wallet addresses
Ensuring the security of your crypto assets involves adopting best practices when dealing with wallet addresses. Here are some techniques to consider:
- Double-check before sending: Always double-check the recipient's crypto wallet address before initiating a transaction to avoid irreversible mistakes. And verify that you've copied the correct wallet address when you want to receive crypto.
- Use reputable wallets: Choose well-established wallets with a proven track record for security and privacy. Research and read user reviews before selecting a crypto wallet provider to store crypto.
- Backup your private keys: Securely store your wallet's private key (or recovery phrase) offline, and never take screenshots or save it in the cloud.*
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Strengthen the security of your wallet by enabling secure 2FA where possible. This adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Keep software updated: Regularly update your wallet software to benefit from the latest security features and patches. Digital wallets without the latest updates may be more vulnerable to security breaches.
*Losing access to your private key means losing access to your funds, and anyone with the private keys can gain access to your crypto. Your public key, however, is safe to share.
For more cryptocurrency security tips, view our guide: 10 steps to a safer Web3 experience
Frequently Asked Questions about Wallet Addresses (FAQs)
What happens if you send crypto to the wrong address?
The irreversible nature of cryptocurrency transactions means that sending crypto to the wrong address will result in loss of funds. Always double-check the accuracy of the recipient's wallet address before initiating a transaction.
Can I use the same address for multiple transactions?
It's recommended to use a new address for each transaction. This practice enhances privacy and security by preventing the linkage of multiple transactions to a single address.
Can I change my crypto wallet address?
In most cases, no. Your wallet address is generated based on your private key, and changing it would require a new private key. However, you can generate a new address within the same wallet for different crypto transactions (and certain wallet providers may even do this automatically).
Why did my wallet application generate a new address for me?
Some software wallets will generate a new address for each transaction. This is generally practiced in the name of privacy, security, and anonymity, since a rotating address can make it more difficult to trace blockchain transactions back to a single user.
Are wallet addresses case-sensitive?
For certain blockchains, some wallet addresses may be case-sensitive. Always ensure that you enter the address exactly as it is provided to you to avoid any errors when sending and receiving cryptocurrency.
Can I share my wallet address publicly?
Yes, sharing your cryptocurrency wallet address publicly is safe, as it only allows others to send funds to your wallet. However, do not share your private keys or any other sensitive information.
What's the different between a private key and public key?
Crypto wallets use a two key system to manage funds securely. A public key can be shared with others to receive cryptocurrency, while a private key is a secret code that grants you access to manage and send your funds.
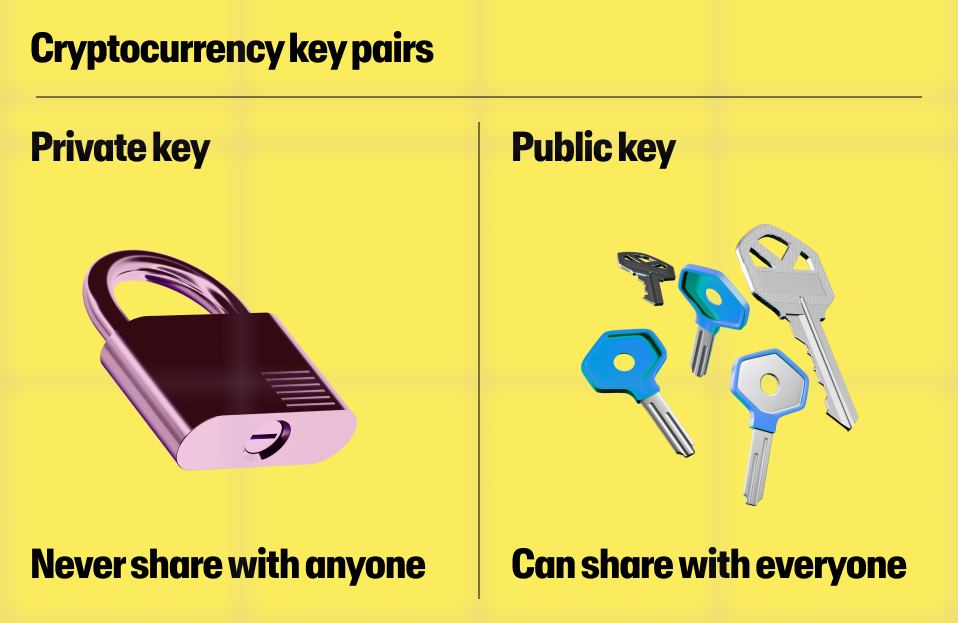
For more information on keys, view our article, Public Key vs Private Key
How long can a wallet address be inactive?
Public wallet addresses for cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin typically don't have an expiration date or become inactive. As long as you have the private key or recovery phrase, you can access your funds at any time.
Can you receive crypto from multiple senders at once?
Yes, if you want to receive cryptocurrency from multiple senders at the same time, you can! There is no limit to how many transactions a wallet can receive at once, other than blockchain network congestion.
Start your crypto journey with MoonPay
Now that you know a bit more about crypto wallet addresses, you may want to explore them for yourself. To get started, simply buy cryptocurrency via MoonPay using your credit card or any other preferred payment method.
MoonPay's widget offers a fast and easy way to buy Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many other cryptocurrencies. MoonPay has partnered with several leading non-custodial wallet providers like Ledger, MetaMask, Exodus, Trust Wallet, to make it easier to self-custody your crypto.
MoonPay also makes it easy to sell crypto when you decide it's time to cash out. Simply enter the amount of the token you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.

.png)