What is HBAR? An introduction to Hedera Hashgraph
Hedera’s hashgraph algorithm consensus mechanism is gaining popularity. But what exactly is Hedera and its native token HBAR?
By Geoffrey Lyons
Hedera is one of those developments in crypto where the more one learns about it, the more potential is seen.
Curious newbies can go down an extensive rabbit hole, starting with the articles on Hedera’s own site and eventually graduating to the dozens of YouTube videos featuring its charismatic and cerebral inventor, Dr. Leemon Baird.
We’ve put together this brief overview of the Hedera network, its native cryptocurrency HBAR, and how hashgraph technology differs from blockchain.
What is Hedera (HBAR)?
Hedera (HBAR) is form of distributed ledger technology called a hashgraph. Similar to a blockchain, a hashgraph is a consensus algorithm whereby a community of users agree on the order of completed transactions.
Unlike a blockchain, however, it works slightly differently:
How is Hedera different from other blockchains?
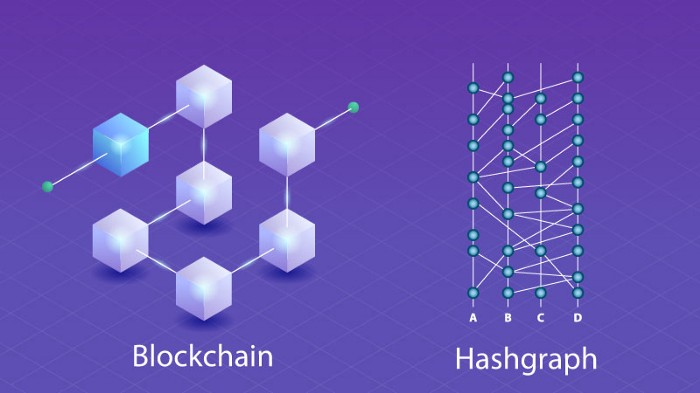
With blockchain, confirmed blocks form a single chain, so if two blocks are created at the same time, one block will be discarded. Hashgraph, on the other hand, is 100% efficient in that the equivalent of a block is never tossed away—it’s always used to achieve consensus.
With hashgraph, all the transaction branches are stitched together into a unified whole (see illustration), resulting in fewer wasted cycles for the network's nodes.
Computer science enthusiasts will also appreciate the fact that the hashgraph algorithm is “Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant”, a status derived from the Byzantine General’s Problem.
The benefit of being ABFT is that Hedera is able to achieve finality. This means that transactions are final in seconds without the need to wait for additional block confirmations in a probabilistic consensus like blockchain.
More can be read about that here, but suffice it to say that these and other major technical differences are what distinguish hashgraphs from blockchains.
Because of these unique properties, Hedera, currently the only distributed ledger technology based on the hashgraph algorithm, brands itself as a “third generation public ledger” (first and second generations are Bitcoin and Ethereum, respectively).
Perhaps the network’s most standout feature is the use of what it calls the "gossip about gossip" protocol.
What is the “gossip about gossip” protocol?
The hashgraph algorithm works by spreading what Hedera’s inventor, Dr. Leemon Baird, calls “gossip about gossip”.
So what is gossip?
“Gossip just means when computers randomly call each other,” says Baird. He explains that any given node in a network can randomly communicate with another node all the information the latter doesn’t already know. The reason this method is so popular in computer science, he says, is because it’s incredibly fast and efficient.
“How fast does a juicy rumor spread through the grapevine in a typical office?” he says. “That’s the gossip protocol.”
Gossip about gossip essentially means that the information being gossiped about is the gossip itself. For example, whereas gossip is telling someone information you know, gossip about gossip is when that information is the fact that you talked to someone else — information that can extend back to the very first conversation (or in Hedera’s case, the very first transaction).
One would assume that it would take a lot of time and energy for computers to share so much information with one another, but according to Baird “gossip about gossip” is incredibly energy efficient. In his 2016 paper introducing the concept, he writes that the protocol “uses very little bandwidth overhead beyond simply gossiping the transactions alone.”
Each message just has to remember two other messages using cryptographic hashes, meaning that when a message is sent, all that’s being sent is two hashes.
Add to the mix a list of transactions, and there’s a working protocol to transact Hedera (HBAR), Hedera’s native token that powers the network’s decentralized applications and, like other Proof of Stake currencies, to reach consensus on transactions.
Who created Hedera?
As mentioned, Hedera was founded by the inventor of the hashgraph, computer scientist Dr. Leemon Baird. Baird has over 20 years of experience running successful start-ups, has been a senior scientist in several labs, and spent time as a Professor of Computer Science at the Air Force Academy.
He earned his PhD in Computer Science from Carnegie Mellon University, widely regarded as one of the top universities in the field, and is co-founder of Swirlds, a successful software company that has patents for the hashgraph.

The network is managed by a Global Governing Council of organizations that have invested in it, including Boeing, Google, IBM, and The London School of Economics.
The more Hedera attracts the attention of such reputable institutions, the more it boosts its reputation as a trusted network. To give an idea of just how well regarded it is, England’s National Health Service recently used it to keep records of its COVID vaccines. For one of the world’s leading health services to rely on Hedera in such turbulent times as these is a major vote of confidence.
Hedera quick facts
- 50 billion total supply of HBAR
- 10,000 transactions per second
- 3.2 second transaction confirmations
- $0.0001 average consensus fee
- 55 million transactions per day
Where to buy HBAR
You can buy HBAR via MoonPay or through any of our partner wallet applications with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods. Just enter the amount of HBAR you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order.
Users can also top up in euros, pounds, or dollars and use MoonPay Balance when buying Hedera (HBAR) and other cryptocurrency tokens. Use your balance to enjoy lower transaction fees, quicker processing times, and better approval rates.
Swap HBAR for more tokens
Want to exchange HBAR for other cryptocurrencies like Ethereum and Bitcoin? MoonPay allows you to swap crypto cross-chain with no processing fees (network fees apply), directly from your non-custodial wallet.




.png)
