What is a DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization)? DAOs explained
Here are some things you need to know about decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), one of the most groundbreaking innovations that blockchain has delivered.
By Sankrit K
Think of the power that someone like Elon Musk has. He can make whatever changes he wants to his company, and you, as a user, have little to no say in it. That's centralization.
Most companies today have a centralized structure, with a small group of people at the top making all the decisions.
Now, imagine an organization where there is no boss. No one person or group is in charge. Decisions are made democratically by the users.
That's decentralization, and that’s where DAOs come in.
In this article, we take a deep dive into Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, their history, how they work, and provide some examples of successful DAOs.
What is a DAO?
A DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) is a type of digital organization that runs on decentralized ledger technology, such as a blockchain. It's an organization with no central authority or single leader. Instead, it's run by code that is stored on a decentralized network.
The code is the law, and includes all the rules and regulations the DAO must follow. These rules can be anything from how to spend money to what kind of projects to pursue.
Using smart contracts (self-executing lines of code) to run the organization means it doesn’t have a centralized point of control.
While it may appear that DAOs lack leadership, in fact DAOs are powered by tokens, which give users voting rights. The more tokens you have, the more voting power you get. This allows users to have a say in how the DAO is run and what decisions it makes.
History of DAOs
The idea to create an organization that uses Distributed Ledger Technology to run itself was inspired by the decentralization of currencies. It was a groundbreaking idea in 2016 that would take the budding web3 world by storm.
Christoph Jentzsch and Simon Jentzsch created the world's first DAO, called "The DAO".
The Rise and fall of The DAO
The DAO was the very first Decentralized Autonomous Organization. It was created on the Ethereum network by the Jentzsch brothers in 2016 and raised over $120 million in funding, making it the largest crowdfunding in history at the time.
The DAO was intended to be a decentralized venture capital fund that would invest in Ethereum-based projects. Users could buy DAO tokens with Ethereum and use these tokens to vote on which projects the organization should invest in.
The goal was to create a completely decentralized way of funding Ethereum-based projects.
Unfortunately, The DAO was hacked just a couple of months after it was created, losing around $50 million. This could have been prevented had the community paid more heed to Emin Gün Sirer, a professor at Cornell University who spotted The DAO's vulnerability early on.
The attack was made possible because of a flaw in the code, which the hacker exploited to steal the funds. This event stirred controversy in the cryptocurrency community and led to a hard fork in the Ethereum network.
The hard fork allowed users to retrieve their funds, but also created a new cryptocurrency called Ethereum Classic (ETC).

Ethereum and Ethereum Classic are both still active today and have different philosophies. ETH is focused on being a decentralized platform for running smart contracts, while ETC focuses on being a decentralized currency.
What's important to note is that even though The DAO was hacked, the code worked exactly as it was supposed to. The hackers did not break the code, but rather exploited a loophole that anyone with far less technical expertise could have done.
This event led to a lot of discussion about the safety of DAOs and whether or not they are truly secure.
Despite the hack, The DAO showed that a completely decentralized organization was possible. Since then, many other DAOs have been created. Some of them are successful, while others have failed. We will take a look at a few of them later in the article.
Funds lost but lesson learned
The hack of The DAO was a big setback for the Ethereum community, but it was also an important lesson. It showed that even though DAOs are decentralized and autonomous, they are not invulnerable to attack.
It also showed that code is the most important element in a DAO. If the code is not secure, neither is the DAO.
How do DAOs work?
A DAO is created when someone writes its foundational code and launches it on a decentralized network. The code contains all the rules and regulations that the DAO will follow.
These rules can be anything from how the DAO is funded to how decisions are made. The rules of the DAO are enforced by smart contracts. A smart contract is a piece of code that automatically executes when certain conditions are met.
For example, a smart contract could be used to send funds from one person to another when a purchase is made. Or it could be used to vote on projects the DAO should invest in.
Smart contracts make it possible for a DAO to exist without any centralized authority.
But what if the DAO needs to change or evolve as time passes?
Can a DAO evolve?
The code of a DAO can be changed if the holders of the DAO tokens vote to do so. This is one of the advantages of having a democratic and decentralized organization: The members can change the rules if they think it’s necessary.
But changing the code can be a risky proposition. If the code is not well-written or tested properly, this could have disastrous consequences for a DAO, which is exactly what happened with The DAO.
That’s why it’s important to have a team of experienced developers working on any DAO code. These developers can try to spot any potential flaws with the code and fix them before the DAO is launched.
Ideally, the code should also be audited by an independent and reputable third party.
Advantages of DAOs
DAOs offer several advantages over traditional, centralized organizations:
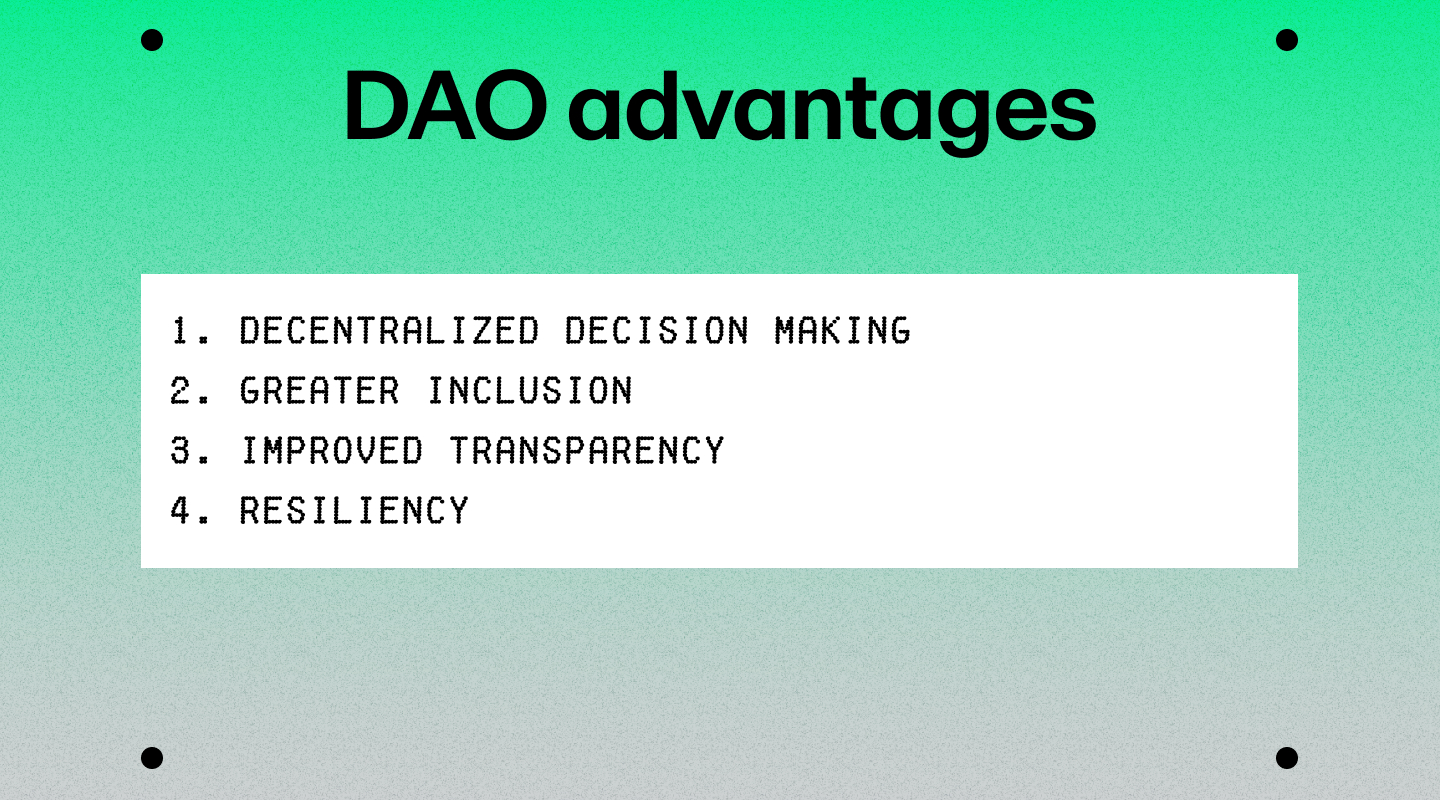
Decentralized decision making
In a traditional top-down model, decisions are controlled by a small group of people at the top. This can lead to many problems including corruption and nepotism.
DAOs, on the other hand, are decentralized so all members have a say in decision-making and their vote is proportional to the number of governance tokens they hold.
The consensus mechanism used by a DAO to make decisions can take different forms, including a simple majority vote or a more complex system like liquid democracy.
Greater inclusion
Not only do governance token holders get to vote on proposals, but any holder can come up with a proposal for a DAO, regardless of their status.
This contrasts with traditional organizations, in which usually only a select few individuals get to make significant decisions or come up with significant proposals.
Improved transparency
All proposals and votes are recorded on the blockchain. This makes it impossible to tamper with the data or hide anything from the public.
Because all decisions are made through a transparent voting process, it’s easier to hold DAO members accountable for their actions.
Resiliency
In a centralized organization, data may be stored in central locations. This could make it easier for hackers to target the organization and steal sensitive information.
DAOs, on the other hand, are decentralized and distributed. This means that there is no central point of failure. Even if one node in the network goes down, the rest of the network will continue to function.
In this way, the decentralized infrastructure of DAOs makes them more resilient to individual points of failure.
Disadvantages of DAOs
DAOs are a new and relatively untested organizational model. As with any new technology, there are certain risks and disadvantages that need to be considered.

Loss of control for members
In a DAO, all decisions are made through a transparent voting process. This means that members have to give up some degree of control over the organization.
There is also a risk that the voting process could be manipulated by people with a majority of tokens. This could lead to decisions that are not in the best interests of the organization or certain members.
No room for confidentiality
Enterprises spend a large chunk of their revenue on research and development. Some companies today are thriving because their research and development findings are strictly confidential, which gives those companies a competitive edge.
In a DAO, however, all the data is stored on a public blockchain. This makes it difficult to keep information secret, as all information about the inner workings of the DAO are publicly available on the blockchain.
While this open-source nature allows the community to improve existing rules, it could also lead to competitive advantages being lost or copied.
Complicated governance structure
The governance structure of a DAO can be convoluted for beginners. This can make it difficult for members to understand how the organization works and make it hard to reach a consensus on important decisions.
Risks associated with smart contracts
DAOs are only as good as the smart contracts that run them. If there is a bug or vulnerability in the smart contract, this can have grave implications for the organization.
For example, a smart contract bug or vulnerability could lead to tokens being stolen from the organization or give a hacker the ability to pass a proposal even if the majority votes against it.
Threat from whales
In a DAO, whales (people with a lot of tokens) have a disproportionate amount of power. This could lead to them having too much influence over the organization.
It could also be possible for whales to manipulate the market by buying and selling large amounts of tokens. This could cause the price of the tokens to fluctuate wildly, which could be bad for the organization.
Tools to create a DAO
Creating a DAO is not an easy task. It requires careful planning and a solid understanding of blockchain technology and smart contracts.
There are tools that can make this process easier. Here are a few DAO tools to consider:
- Aragon - Ideal for projects with a few in-house developers
- Snapshot - Flexible and affordable governance platform
- Juicebox - Very beginner-friendly funding protocol
- DAOstack Alchemy - Affordable DAO creation app
- Colony - Create a DAO in 90 seconds
- Metaphor - Simplified DAO onboarding
- Upstream Collectives - First mobile DAO product
Examples of successful DAOs
MakerDAO

MakerDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization that runs on the Ethereum blockchain. It is responsible for the Dai stablecoin, which is pegged to the US Dollar.
The Dai stablecoin is used to collateralize loans on the decentralized lending platform MakerDao. When a user wants to take out a loan, they deposit their DAI as collateral. If the value of their DAI falls below a certain threshold, the loan is automatically liquidated and they lose their collateral.
The DAO itself, however, is governed by the Maker token (MKR). MKR has three roles in MakerDAO:
- Governance token: Helps distribute voting power
- Utility token: Pays transaction fees in the Maker ecosystem
- Resource for recapitalization: Compensates shortfall of value in the system
Uniswap

Uniswap is a decentralized exchange built on the Ethereum network. It allows users to trade ETH and ERC-20 tokens without the need for a centralized exchange.
The Uniswap protocol is governed by the UNI token. UNI was created to incentivize users to provide liquidity to the platform and to reward them for their contribution.
UNI holders can also vote on proposals that will determine the future of the protocol. To submit a proposal yourself, you need to hold at least 0.25% of UNI's total supply.
Aave

Aave is a decentralized borrowing and lending platform in the Ethereum ecosystem that allows users to deposit their crypto assets to earn interest. It also allows users to take out loans against their deposited assets.
The Aave protocol is governed by the AAVE token. The AAVE token gives holders the right to vote on proposals that will determine the future of the protocol. It also entitles them to a share of the protocol's revenue.
Key takeaways on DAOs
- A DAO is a decentralized organization that is run by a smart contract on a blockchain.
- DAOs are trustless, transparent, and inclusive. They have the potential to revolutionize the way organizations are run.
- DAOs are also complicated and vulnerable to attack. As such, they require careful planning and a solid understanding of blockchain technology and smart contracts.
Start your DAO journey
To become a member of a DAO, you will need to hold their governance tokens. Only then will you be able to vote on proposals or submit one yourself.
With MoonPay, you can buy governance tokens like AAVE, MKR, UNI, and more with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods.
Just enter the amount of crypto you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order.