What is crypto staking? A guide to staking cryptocurrency in DeFi
Want to do more with your crypto than just holding? Staking cryptocurrency could be the solution. Learn more about this key DeFi process here.
By Corey Barchat
It's standard practice for banks in many countries around the world to offer customers the opportunity to earn interest on certain deposits.
But what if you could also be paid to hold onto your cryptocurrency?
The good news is, you can. In the cryptocurrency world, it is possible to generate rewards from the cryptocurrency you hold through a process known as "staking."
In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of crypto staking, how it works, why it is important in decentralized finance (DeFi), and how you can get started staking cryptocurrency to potentially earn rewards.
What is crypto staking?
Crypto staking is the process used in Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain networks to validate transactions on the network and involves locking up your cryptocurrency to smart contracts, where there is potential to earn rewards on your staked assets.
The third party custodian that holds your coins can be a cryptocurrency exchange, a wallet provider, or any staking platform that runs on a Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain.

To understand staking further, we need to understand the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism used in blockchains.
Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchains
Proof of stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism most blockchain platforms use to achieve distributed consensus. In Proof of Stake, validators are responsible for confirming transactions, creating new blocks, and maintaining the security and integrity of the blockchain.
In return for their efforts, they earn rewards in the form of additional cryptocurrency tokens.
One advantage of Proof of Stake systems over Proof of Work (PoW) is that PoS requires far less energy and, therefore, is more environmentally friendly. Proof of Work cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin involve miners solving complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and secure the network.
In Proof of Stake, anyone can become a block validator and participate in validating transactions and creating blocks. By contrast, PoW requires expensive specialized hardware, such as ASIC miners, which can be difficult for new entrants to obtain.
The PoS concept was first proposed in 2012 by Sunny King and Scott Nadal for the PPCoin cryptocurrency in a paper titled "PPCoin: Peer-to-Peer Crypto-Currency with Proof-of-Stake."
Since then, many blockchains have implemented Proof of Stake (or their own variations of PoS), including Ethereum (ETH), Eos (EOS), Cardano (ADA), Solana (SOL), Algorand (ALGO), Tezos (XTZ), Near Protocol (NEAR), and Cosmos (ATOM).
Recommended reading: Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
How does staking work?
When you stake your crypto, you're essentially locking it up in a smart contract to be used to keep the network up and running. In return, you receive a portion of the new coins created via the block reward. In many protocols, you can request to unlock your tokens at any time but you may have to wait for a certain amount of time (hours, days, weeks, etc.) before your crypto is available to you to be used for other purposes.
The mechanics of crypto staking are relatively straightforward:
- Cryptocurrency ownership: To participate in staking, you'll need to own a certain amount of the cryptocurrency native to the relevant blockchain network.
- Staking: You lock up or "stake" your cryptocurrency in a dedicated crypto wallet or to a smart contract (which may allow you to hold your cryptocurrency in your own wallet), making it temporarily inaccessible for trading or withdrawal.
- Validation and staking reward: As a staker, you contribute to validating transactions and creating new blocks. In return for your contribution, you may receive staking rewards, which are typically distributed regularly, and could include transaction fees paid by other users.
- Network governance: Many PoS blockchains allow stakers to participate in decision-making, enabling them to vote on network upgrades and changes.
The staking details will vary based on the specific cryptocurrency blockchain being used. You may also need to keep a minimum amount of digital assets in your wallet to be eligible for staking rewards.
By locking up your coins, you're essentially pledging collateral to the PoS network to become a block producer (or validator). Then, when a new block is produced, the validator who helped produce that block receives a reward.
Now, let's see how you can get started with staking crypto.
How to start staking crypto in 3 easy steps
Here are three easy-to-follow steps to start staking your crypto today.
Step 1: Choose your PoS cryptocurrency
Not all cryptocurrencies are available for staking, so first you'll need to decide which coin you want to stake.
Choosing the right coin is not easy, but we've put together a list of popular cryptocurrencies that can be staked:
- Ethereum (ETH): The second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, known for its smart contract functionality.
- Solana (SOL): A high-performance blockchain known for its speed and scalability, supporting decentralized applications (dApps).
- Polkadot (DOT): A multi-chain network that enables interoperability and communication between different blockchains.
- Avalanche (AVAX): A platform designed for creating custom blockchain networks and decentralized applications.
- Cosmos (ATOM): A blockchain focused on interoperability, connecting various blockchains to create a more inclusive web3 ecosystem.
- Near Protocol (NEAR): A blockchain platform designed for developers to build decentralized applications.
- Algorand (ALGO): A scalable and efficient blockchain designed for secure and fast transactions.
- Tezos (XTZ): A blockchain featuring self-amendment and on-chain governance to adapt and evolve over time.
This list is by no means exhaustive. As per CryptoSlate, there are over 2400 PoS-based cryptocurrencies, with more created every day.
With MoonPay's reliable fiat-to-crypto on-ramp, it's easy to buy many Proof of Stake cryptocurrencies using a card.
Step 2: Transfer your crypto to a supported wallet or exchange
Staking is a huge component of decentralized finance, with a market cap that ranges in the dozens of billions of dollars. As such, the majority of crypto wallets and exchanges now support staking directly on their platforms.
If you wish to stake crypto, you’ll need to check to confirm that the CEX or wallet provider you use offers staking functionality. Once you confirm that staking is available, you should transfer the funds to the relevant platform, if you have not done so already (in the event you’re sending funds from an external wallet that does not offer staking).

As always, it's best to research all available options and choose a secure and reliable wallet that's right for you. When you buy crypto from MoonPay, purchased cryptocurrency can be directly deposited into your non-custodial wallet.
Some non-custodial wallet providers that offer staking include:
Step 3 - Join a staking pool
Staking pools are essential services to help you stake cryptocurrency held in a non-custodial wallet without having to go through the hassle of setting up your own validator nodes.
To join a staking pool, just follow these basic steps:
- Select a reputable staking pool (after doing your own research)
- Connect your wallet to the pool
- Stake your tokens in the pool
- Receive your staking rewards proportionate to your contribution amount
Similar to mining pools, staking pools combine the cryptocurrencies of many token holders and stake those combined assets on behalf of the token owners, for a small fee. The rewards are then distributed among the participants based on the percentage of their contribution.
Staking pools have become increasingly popular as they help overcome crucial barriers to staking cryptocurrencies such as technical knowledge, server availability, and capital requirements.
Below are a few staking pools currently offering services:
Did you know? In addition to cryptocurrency, you can also stake NFTs
What are the benefits of staking crypto?
There are several benefits of cryptocurrency staking, which have contributed to its popularity in the web3 community.
1. Earn staking rewards
If you believe in the long-term potential of a cryptocurrency, then staking could be an alternative way to earn passive income through your cryptocurrency holdings without needing to buy more (or mine it). Keep in mind you will earn rewards in whatever cryptocurrency you choose to stake.
For example, let's say you want to stake ETH, then you will receive rewards in ETH. These rewards are based on a percentage of the total amount of Ether being staked by all participants in the pool, and are generally paid out on a regular basis, such as daily, weekly, or monthly.
2. Secure the network
Stakers play a critical role in maintaining the security of the blockchain via financial commitment and active participation. This makes it less likely for malicious actors to disrupt the network, ultimately benefiting all users and helping to prevent fraud and 51% attacks.
The more diverse the pool of stakers is, the more economically costly it is for a would-be hacker to control the majority of the staking power.
3. Greater decentralization
Staking promotes decentralization by allowing more individuals to participate in the network validation process.
Unlike PoW, which often relies on a select group of centralized miners, PoS networks are usually more inclusive, as anyone can stake tokens and contribute to the network.
4. Environmental impact
Mining cryptocurrency is a resource-intensive process that requires a lot of energy and leaves a huge carbon footprint for every transaction.
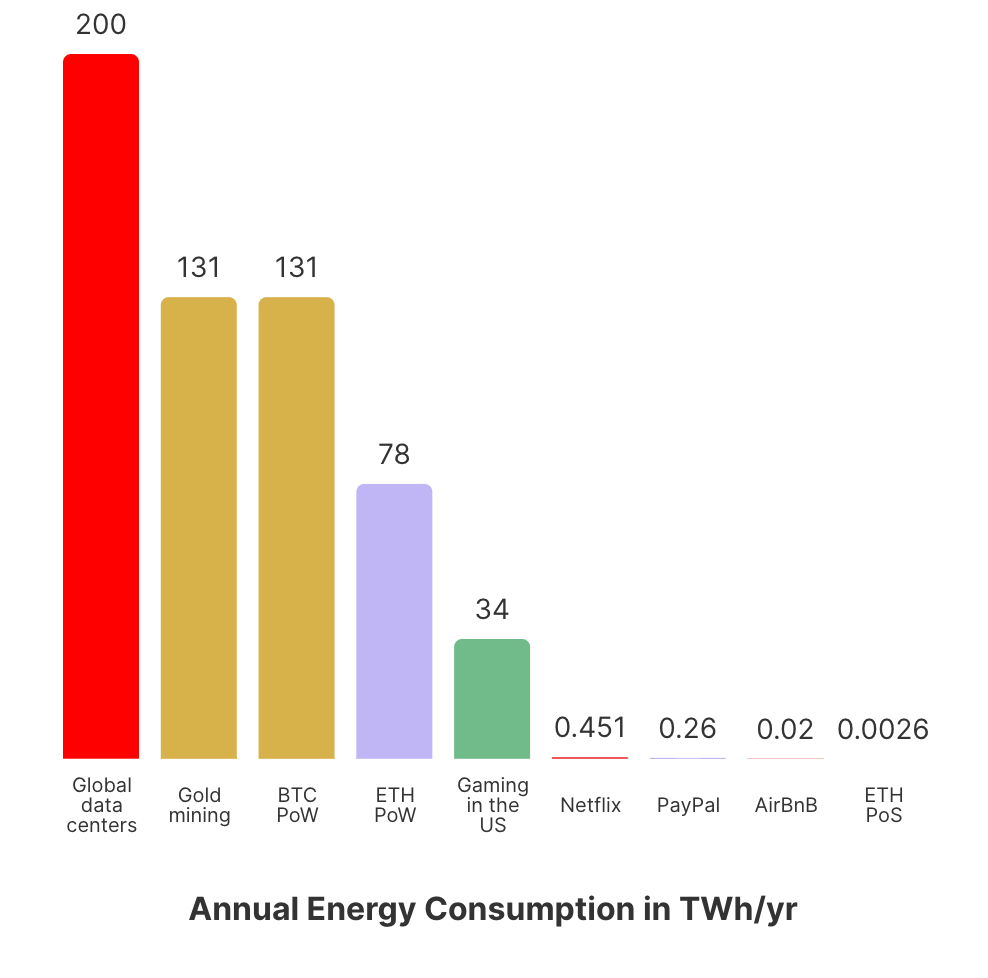
Mining blocks using PoS, on the other hand, reduces carbon emissions by 99.9%, significantly reducing the negative impact of cryptocurrency on the environment.
5. Network participation
Many Proof of Stake blockchains implement network governance, giving stakers a say in important decisions about protocol upgrades, network changes, and other governance-related matters. This democratic approach allows the community to collectively decide the direction of a blockchain network and its development.
Did you know? You can pay with Proof of Stake cryptocurrency
What are the risks of staking crypto?
While there are several benefits, there are also potential risks of staking cryptocurrency. It's important to be aware of these downsides when considering whether you want to stake.
1. Cryptocurrency volatility
The cryptocurrency market is known for its price volatility, and staking may prevent you from being able to sell staked cryptocurrency quickly.
The value of your staked assets can fluctuate, and you could end up with lower valued crypto assets if the token's price declines while your tokens are staked and locked to a smart contract. When you stake crypto you also risk missing out on any potential price gains in the market.
2. Slashing penalties
Some Proof of Stake blockchain networks have a slashing mechanism in place to penalize validators for malicious behavior or other network disruptions. If a validator fails to fulfill their responsibilities or engages in harmful actions, they could lose a portion of their staked coins which means you could lose your staked assets.
Although this risk is generally low if you stake crypto in a reputable pool, it is not uncommon for even the best validators to get their stake slashed, even if it happens unintentionally.
3. Greater centralization
While PoS networks are generally more decentralized than their PoW counterparts, they can still face centralization risks.
If a small number of stakeholders dominate the network, it may undermine decentralization efforts and community-driven decision-making.
4. Technical vulnerabilities
Technical issues can arise in the staking process, such as wallet vulnerabilities or software bugs. These technical risks can result in the loss of your staked assets or reduced crypto rewards.
5. Increased illiquidity during lock-up periods
Staking typically involves a lock-up period, during which your staked cryptocurrency are inaccessible. The reason being that most staking services release your funds only hours or days even after you have unstaked them.
This can be a barrier in emergencies if you need quick access to your digital assets, or if you'd like to use your crypto for other purposes, such as trading.
How are staking rewards calculated?
Staking rewards are typically calculated based on the following factors:
- Amount: The more cryptocurrency you stake, the more you maximize rewards.
- Duration: Some networks reward longer-term stakes with higher returns.
- Network rules: Each PoS network may have unique rules and parameters for reward distribution.
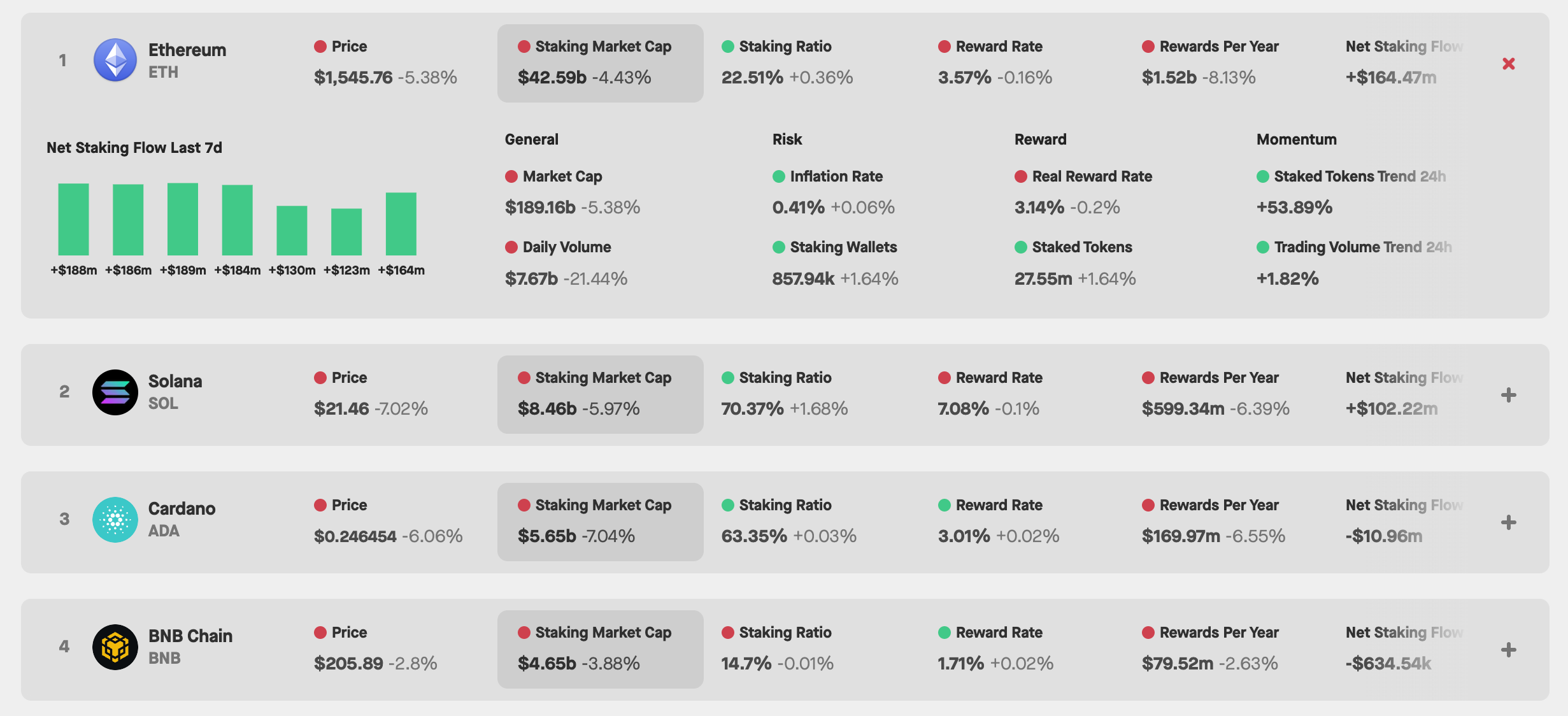
Earning staking rewards will vary significantly between different PoS networks, so it's important to research the specifics of the network or protocol you're interested in.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about staking
1) What if a validator tries to pass fraudulent transactions as legitimate?
If a validator tries to falsify block production, they could lose a part of their stake through a penalty known as "slashing." This means that validators have a financial incentive to act honestly and produce accurate blocks, as well as motivation to help catch other fraudulent network nodes.
2) How to become a node validator?
A masternode (also known as a "validator node") is a node that helps to verify transactions on a PoS blockchain, though the number of coins required to create a masternode varies from protocol to protocol.
Once you lock in the cryptocurrency, you will start earning rewards as a percentage of the amount staked. In general, the more tokens you pledge, the greater your chances of being chosen by the protocol as a validator.
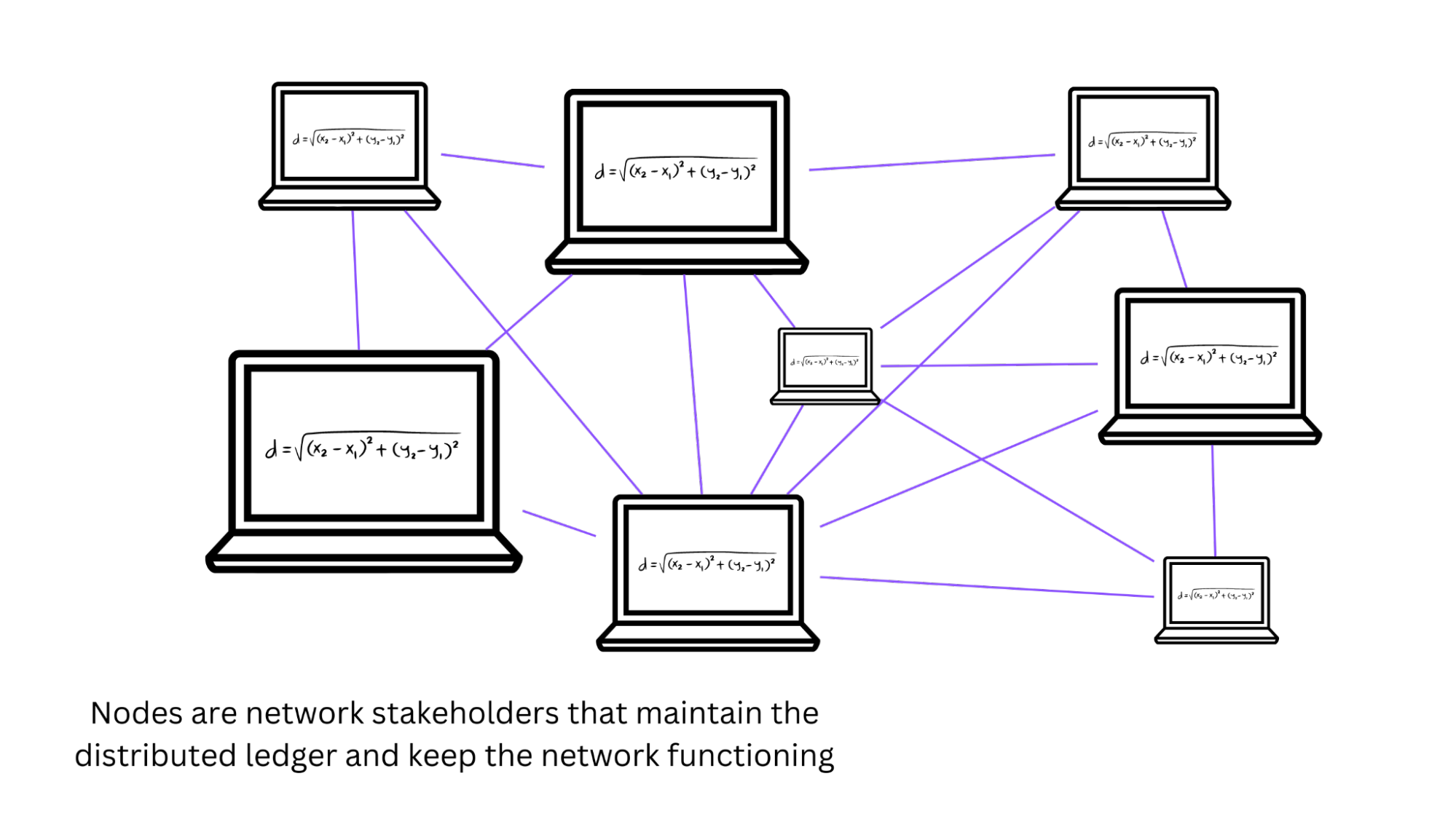
However, it is not practical for everyone to operate a masternode because the minimum value of staking can be substantial. In the case of Ethereum, which requires 32 ETH, the minimum value of the staked assets would be $64,000 if the price of ETH is $1,500 per coin.
3) What is Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)?
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a variation of the traditional PoS model. With DPoS, validators are carefully curated by the project founders, creators, and community. Only these validators are given the privilege to stake crypto and keep the networking running smoothly.
If anyone else wants to contribute to the network and earn rewards, they can do so by lending or "delegating" their coins to one of these chosen validators. These validators then stake the borrowed tokens on others' behalf and give them their rewards after taking a small cut for their services.
4) Can Bitcoin be staked?
Although there are Proof of Work blockchains that incorporate staking, Bitcoin cannot be staked.
Concluding thoughts: Is staking crypto worth it?
As with any investment, you should only stake what you are comfortable with, depending on factors including your financial goals and risk tolerance. There is always the risk of losing your staked assets, in the event that the cryptocurrency's price falls or the validator's stake is slashed.
In addition, you should also be aware of the opportunity cost of staking, as you would be unable to use your crypto for other purposes during lock-up-periods.
If you are comfortable with the risks, staking can be a great way to earn passive income on your cryptocurrency holdings, while helping to secure the network. However, you should always be aware of the risks before making any decisions.
Start your crypto staking journey
To begin the staking process, first you'll need to acquire cryptocurrency. Whether you purchase crypto for staking, hodling, or trading, MoonPay makes it easy.
You can buy Proof of Stake cryptocurrencies via MoonPay or through any of our partner wallet applications with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods.
MoonPay also makes it easy to sell crypto and Proof of Stake tokens like ETH, SOL, and AVAX when you decide it's time to cash out your holdings. Simply enter the amount of cryptocurrency you'd like to sell and enter the details where you want to receive your funds.




.png)