The vast majority of crypto trades take place on centralized exchanges (CEXs) and decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
The former requires a handover of assets to a centralized authority, while the latter requires buyers and sellers to provide liquidity to order books. And on a decentralized exchange, trades cannot be executed efficiently if there’s low liquidity.
This is where Uniswap comes in. Uniswap uses a decentralized trading model called an automated liquidity protocol to improve liquidity and make cryptocurrency trades more efficient. But it's more complicated than that.
In this article, we’ll dive deeper into what Uniswap is, how it works and how it differs from traditional order books and centralized exchanges.
What is Uniswap?
Uniswap is a decentralized cryptocurrency exchange built on the Ethereum blockchain and compatible with Layer 2s like Arbitrum, Base, and Optimism. It pools liquidity and uses a deterministic algorithm to calculate the price of crypto assets, rather than relying on buyers and sellers. This enables traders to make token swaps across all price ranges without running out of coins.
Unlike traditional cryptocurrency exchanges, Uniswap employs an Automated Market Maker (AMM) model, which has revolutionized the way we trade cryptocurrencies. Rather than making trades directly with another party, AMMs make it easier for users to trade tokens against liquidity stored in smart contracts.
At its core, the Uniswap protocol allows users to swap various Ethereum-based tokens directly from a non-custodial wallet, while staying in full control of their digital assets.
How does Uniswap work?
Technically speaking, Uniswap is powered by two smart contracts: the "Exchange" contract and the "Factory" contract. The former handles token swaps (or trades) and the latter adds new tokens to the Uniswap platform.
At its heart, Uniswap is built on several core features that underpin its unique functionality:
- Automated liquidity protocol: Uniswap's automated market maker (AMM) model removes the need for traditional order books and instead relies on liquidity pools to facilitate trades, automatically calculating the exchange rate based on the pool's reserves.
- Permissionless: Uniswap is a decentralized platform, meaning anyone can create a new liquidity pool or add liquidity to an existing one. This permissionless nature helps democratize and decentralize the token exchange process.
- Liquidity provision: Users can swap tokens and provide liquidity to the platform. Liquidity providers receive a share of the trading fees generated by other users performing Uniswap transactions.
- Constant product formula: Uniswap uses a mathematical formula to maintain constant liquidity within its pools. This formula ensures that the product of the reserve amounts for two tokens in a pool remains the same before and after a trade.
Since Uniswap is an ETH-based exchange, you can only swap ERC-20 tokens with each other. To understand how it works, let’s look at the function of its liquidity protocol:
Uniswap liquidity pools
Uniswap's liquidity pools ensure that tokens are always available for trading. These pools are created by users called liquidity providers who contribute both of the tokens in trading pairs, typically in equal value. Liquidity pools enable users to exchange tokens seamlessly, and reward providers with transaction fees for their participation.
How liquidity pools work
Each liquidity pool in Uniswap contains a unique token pair and anyone can contribute liquidity to it. When you provide liquidity to a Uniswap pool, you deposit an equal value of two tokens into the pool.
When the LP mints a pool for the first time, they’ll get x.y tokens, where x and y are the amount of each token they provided. After the first mint, Uniswap calculates the proportion of the pool’s liquidity provided to determine how many liquidity tokens the LP should get.
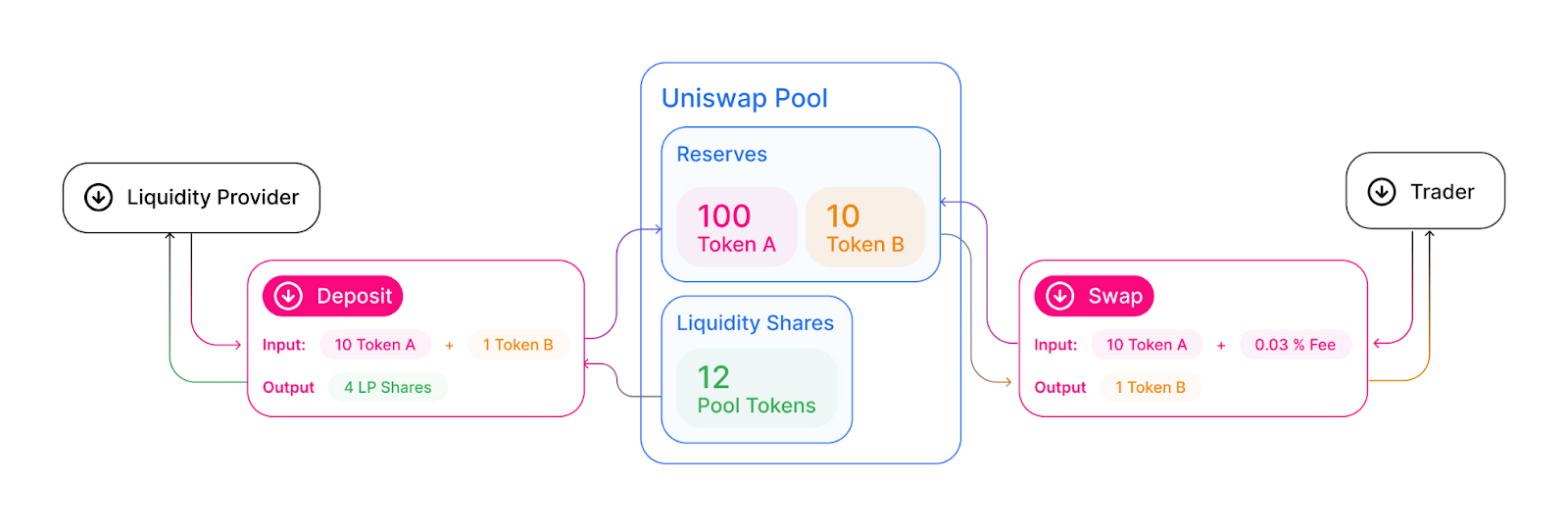
For instance, if you want to create a liquidity pool for ETH and DAI, you would deposit an equal value of both ETH and DAI. The liquidity pool will automatically calculate the exchange rate based on the amount of each token in the pool, and you'll be rewarded with LP tokens earned from other users making trades between Ethereum and Dai on the Uniswap platform.
The role of liquidity providers
Liquidity providers play a vital role in the Uniswap ecosystem. They earn a share of the trading fees generated by the platform, which incentivizes them to participate. It's a way for users to earn passive income while helping to maintain the liquidity of the platform.
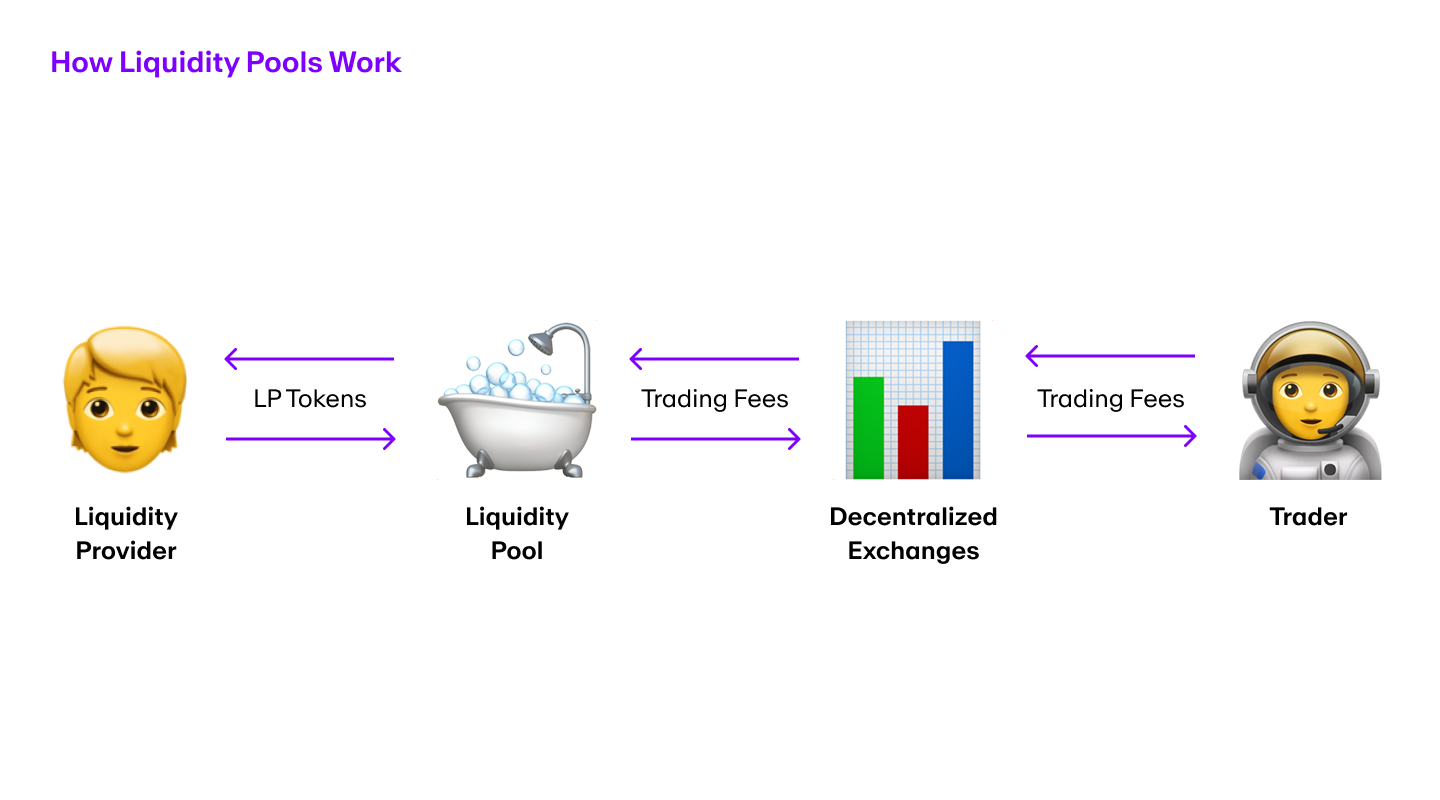
For example, if you provide 10% of the pool’s liquidity, your token will entitle you to 10% of the liquidity available in the pool. In case new tokens are added or removed, Uniswap will mint or burn liquidity tokens to ensure that everyone’s relative percentage share remains the same.
Alternatively, liquidity providers can also sell, trade or transfer their LP tokens, since these are tradable assets. To withdraw liquidity, users can burn liquidity tokens and exchange them for the liquidity in the pool, along with the proportional fee allocation.
Token swapping
Swapping tokens on Uniswap is a straightforward process. Users select the tokens they want to swap, and the platform calculates the exchange rate based on the liquidity pool's reserves. The conversion is executed instantly, making it a user-friendly experience for traders.
For step-by-step instructions to exchange tokens on Uniswap, read our Token Swaps guide.
The Uniswap (UNI) token
What is the UNI token?
UNI is Uniswap's native token, introduced to give users a say in the platform's development and decision-making. As a governance token, UNI gives holders the ability to vote on proposals that shape the platform's future.
Why was the UNI token created?
In 2020, Uniswap launched the UNI governance token, which allowed anyone who held more than 1% of the available tokens to submit and vote on proposals that further the development of the protocol.
The idea behind the launch was to create a system that’s both decentralized and self-sustaining, and prevent users from switching to a competitor DEX, such as SushiSwap, a Uniswap clone.
To compete with Uniswap, SushiSwap started luring users with SUSHI tokens. Uniswap retaliated by minting 1 billion UNI tokens and airdropping them to 150 million users on the network.
Each user—anyone who interacted with the contract, including the 12,000 addresses that had only submitted failed transactions—was eligible to claim 400 UNI tokens at the time, which was roughly equivalent to $1,000.
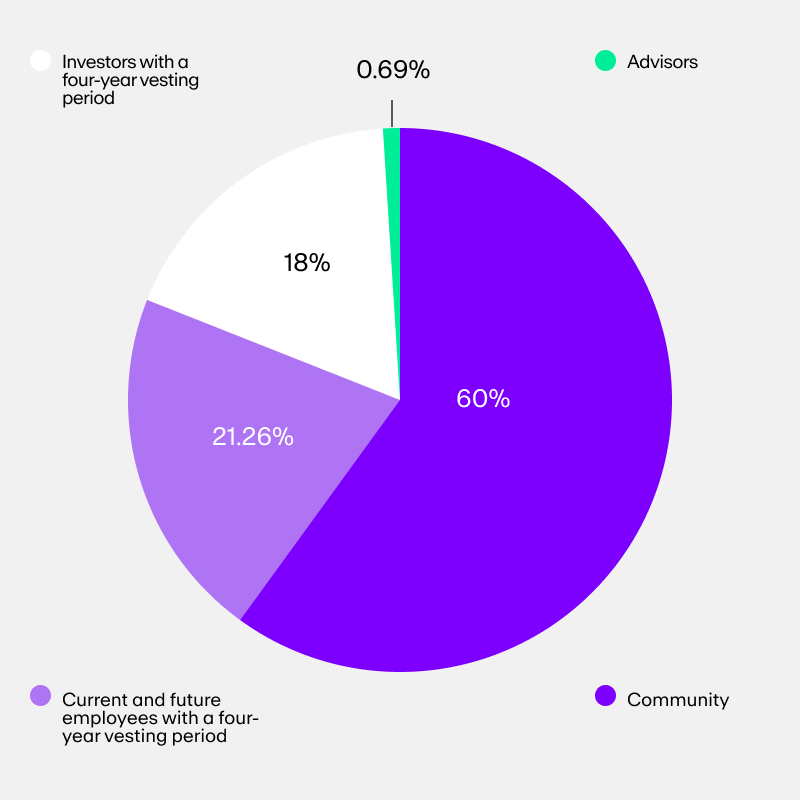
Uniswap (UNI) token allocation (1 billion total)
- 60% to Uniswap community members [600 million UNI]
- 21.26% to team members and future employees with 4-year vesting [213 million UNI]
- 18% to investors with 4-year vesting [180 million UNI]
- .069% to advisors with 4-year vesting [7 million UNI]
How does governance work on Uniswap?
Uniswap operates with a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) structure. This means that decisions about the platform's future are made by UNI token holders through a voting mechanism.
Generally speaking, the more UNI tokens you hold, the more voting power you have. If you're a UNI holder, you can head to the Governance Forum to view, discuss, and vote on newly introduced proposals.
Recently voted UNI proposals
UNI token holders actively participate in shaping Uniswap's future. Some recent proposals voted on include changes to fee structures, grants for development projects, and the introduction of new features to the Uniswap protocol.
This governance model ensures that the Uniswap protocol evolves in a way that aligns with the interests of its community.
How does Uniswap determine token prices?
On the Uniswap platform, a proportional amount of tokens must be deposited or sold when tokens are withdrawn to maintain a balanced liquidity pool. Uniswap does this using a mathematical formula called the constant product formula:
k = x.y
According to this formula, k is a constant and x and y are the ERC-20 tokens being traded.
When the pool is first created, the LP determines this constant k. But once trades start taking place, this value grows or remains the same with every trade.
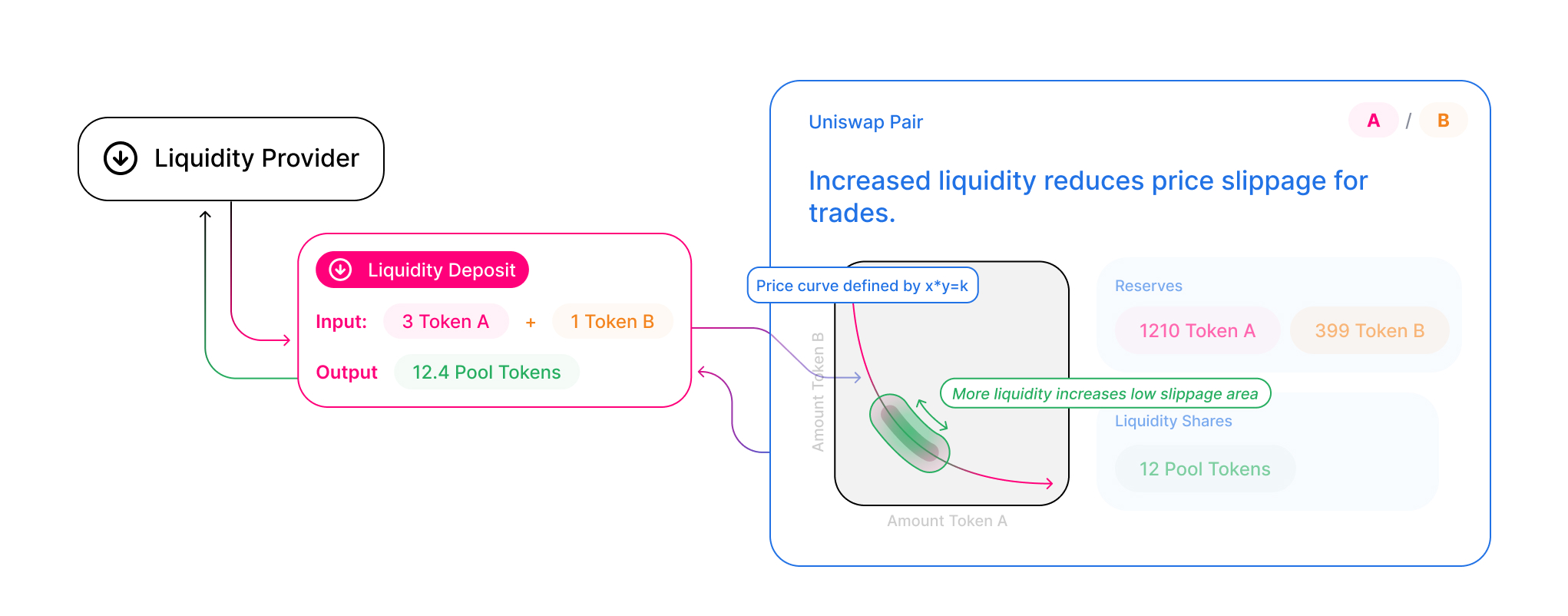
It’s this constant k that helps determine the price of the tokens. Here’s an example to understand this better.
Let’s say Alice deposits 10 ETH and 100 DAI into a liquidity pool. The k value is 10*100 = 1000 and according to the constant product formula, the pool should maintain this value regardless of whether tokens are withdrawn or added to the pool.
Using Uniswap for arbitrage
One unique way to leverage Uniswap is through arbitrage.
Arbitrage in crypto refers to taking advantage of price differences for the same digital asset on multiple exchanges. Uniswap's liquidity pools can be used to identify arbitrage opportunities, allowing traders to exploit these differences to make a profit by buying low on one exchange and selling high on another.
For the Uniswap protocol itself, however, the practice of arbitrage serves a different purpose: It actually helps Uniswap adjust token prices to match the market prices on other exchanges.
Benefits of using Uniswap
Uniswap offers several advantages that have contributed to its popularity over other decentralized exchanges.
Lower fees
Uniswap's fee structure is often more competitive than other exchanges. Users pay a small fee for each trade, which is then shared with liquidity providers. This makes it an attractive option for traders looking to minimize transaction costs, and incentivizes users to contribute to the platform.
Global accessibility
Uniswap is accessible to anyone with an internet connection, and it operates 24/7. This helps break down barriers and allows users from around the world to participate in decentralized finance (DeFi).
No centralized intermediary
Uniswap operates as a decentralized exchange, meaning there's no central authority or intermediary controlling the platform. This mitigates the risk of third-party manipulation, helps prevent centralized hacks, and ensures that users have full control over their funds.
Real-world financial tools
Uniswap has played a significant role in DeFi applications (dApps), such as decentralized lending, where users can borrow and lend digital assets without the need for a central entity. These applications often rely on Uniswap's liquidity pools to ensure that assets can be efficiently traded.
Uniswap risks
While Uniswap offers many benefits, it's essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with using the platform.
Smart contract vulnerabilities
As with any decentralized application, Uniswap is built on smart contracts. While these contracts are generally secure, there's always a risk of vulnerabilities or exploits. Although Uniswap has a strong track record for security, no system is entirely immune to vulnerabilities.
Impermanent loss
Liquidity providers are exposed to impermanent loss, a temporary loss of value that can occur when the price of the two tokens in a pool diverge. Since cryptocurrency prices can change often, impermanent loss will occur whether token prices go up or down during the time that they are kept in the liquidity pool.
Impermanent loss means that a liquidity provider may end up with fewer tokens than they initially deposited, despite earning passive income via trading fees. This risk is inherent in liquidity provision, and is important to consider for potential liquidity providers.
Market volatility
Cryptocurrency markets can be highly volatile, and this can result in rapid price fluctuations, affecting the value of assets held in liquidity pools.
As with any investment or financial activity, users should conduct thorough research and follow best security practices when using Uniswap or any DeFi platform. This could include using hardware wallets, enabling two-factor authentication, and being wary of phishing and other scam attempts.
The history of Uniswap V1 to Uniswap V3
When Uniswap V1 first launched in November 2018, it used the constant product formula k=x.y still used today, though it only supported trades from ETH to other ERC20 tokens.
For example, if you wanted to trade USDC for DAI, you’d first have to convert USDC to ETH, and use the ETH to buy DAI tokens. This was highly inefficient, so Uniswap launched its second version.
Did you know? MoonPay makes it easy to make direct crypto swap transactions like the ones listed above.
Uniswap V2 did away with the condition that you had to convert your ERC-20 tokens into ETH, and enabled traders to create ERC-20 token pairs. Like Uniswap V1, it also used the k=x.y formula to provide liquidity at all price ranges.
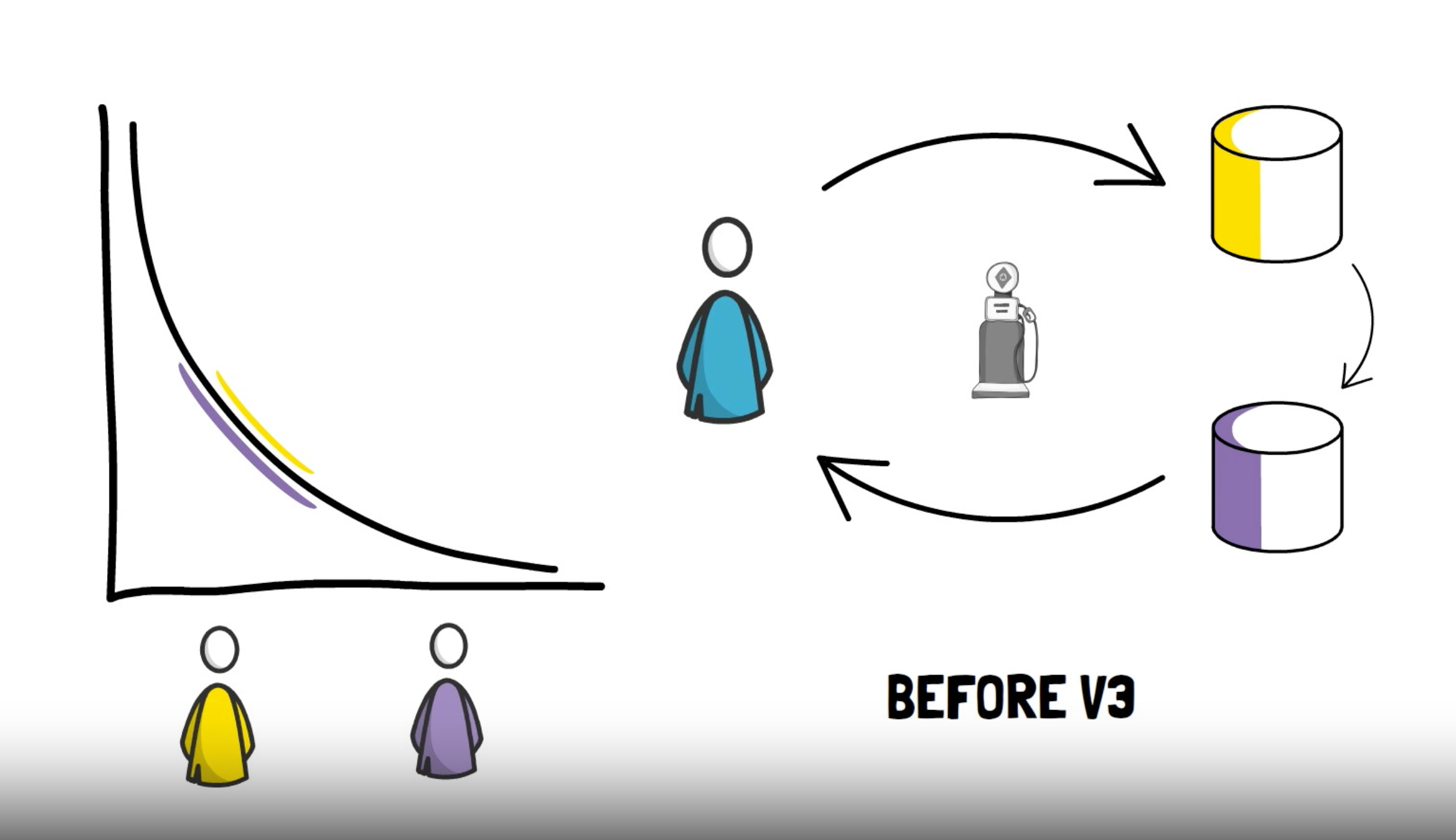
The main aim of Uniswap V2 was to provide liquidity across all price ranges by creating a constant product market, but this resulted in a large amount of liquidity in the pools being unused. This is the problem that Uniswap V3 seeks to solve.
Instead of providing liquidity across the entire price range, Uniswap V3 provides concentrated liquidity across smaller price ranges, called positions. These positions act as constant product pools and maintain just enough reserves to support trading within that range.
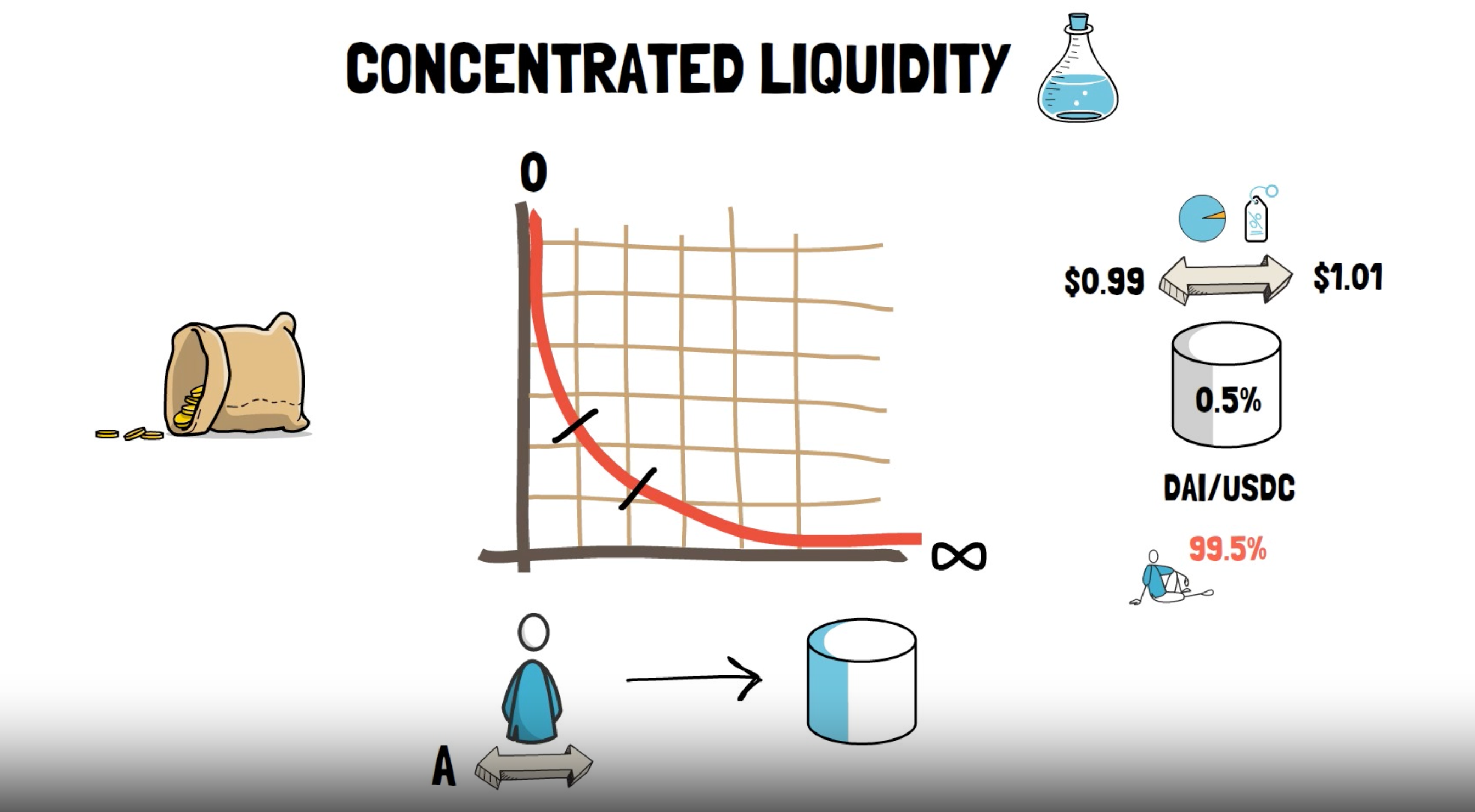
The smaller reserves within the pools are called virtual reserves, and LPs can create as many of them as they want. By doing so, they are creating different positions across different price ranges to improve the usage of liquidity.
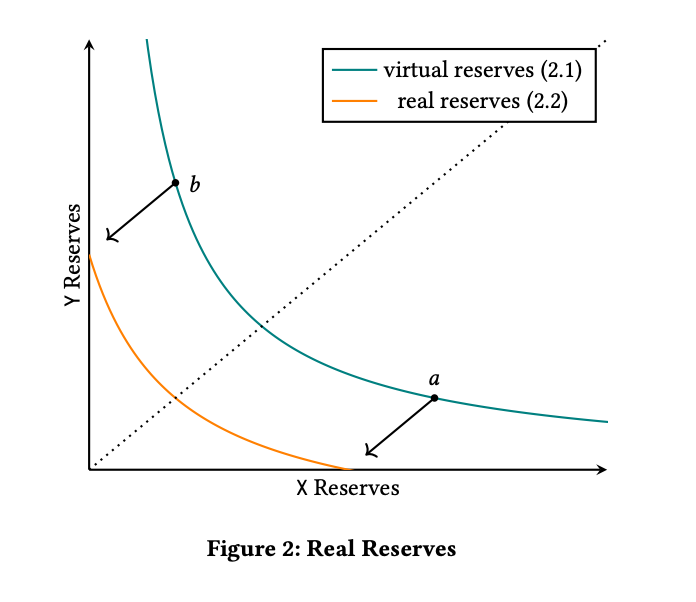
In other words, Uniswap has broken itself down into smaller pools with reserves distributed across the most popular trading price ranges, instead of being a giant token pool with one large reserve.
Uniswap competitors and alternatives
While Uniswap is a pioneer in the automated market maker (AMM) space, it's not the only decentralized exchange (DEX) available. Here are several DEX alternatives:
SushiSwap

SushiSwap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) that began as a Uniswap fork but has since developed its own ecosystem. SushiSwap introduced the concepts of yield farming and staking, allowing users to earn additional tokens as passive income by providing liquidity.
PancakeSwap

PancakeSwap operates on the Binance Smart Chain, offering an alternative to Ethereum-based DEX platforms. It's known for its low transaction fees and has a similar AMM model to Uniswap.
1inch

1inch is a DEX aggregator that sources liquidity from multiple decentralized exchanges, including Uniswap. It aims to provide users with the best available prices by routing trades through various exchanges.
FAQs about Uniswap
1. Is Uniswap safe?
Uniswap is decentralized and therefore not prone to hacker attacks that can steal users’ funds on centralized exchanges (CEXs). Plus, it’s built on Ethereum, so it has the same security properties as the leading Proof of Stake blockchain.
However, no exchange can offer complete security so make sure to do your own research before using any exchange.
2. What can Uniswap (UNI) tokens be used for?
The Uniswap (UNI) token is a governance token that can be used to create and vote on proposals to improve the protocol.
You can also trade it for other cryptocurrencies and sell it to another address to transfer your ownership and governance rights.
3. How to use Uniswap?
To get started with Uniswap, you’ll need to download an Ethereum-based wallet like MetaMask.
Once you’ve downloaded and set up your non-custodial wallet, go to the Uniswap exchange and follow the instructions.
Not sure how to choose a wallet? Read our helpful guide
4. How to claim UNI tokens?
Before you claim your UNI tokens, ensure that you connect the wallet that you previously used on Uniswap. If you’re eligible to claim Uniswap tokens, you’ll see a popup in the top right corner of your Uniswap app.
To claim the tokens and approve the transaction, choose the correct gas fees and click “Claim your tokens” to approve the transaction.
Recommended reading: Ethereum gas fees
5. How is the UNI token price determined?
The price of the UNI token, like most cryptocurrencies, is determined by supply and demand in the open crypto market. Traders and investors can swap UNI tokens on Uniswap and other exchanges, influencing the UNI token price.
The future of Uniswap
Uniswap has established itself as a leading decentralized exchange, offering numerous benefits such as its automated liquidity protocol, lower fees, liquidity pools, and global accessibility. Its governance model allows anyone to actively participate in shaping the platform's future via UNI tokens.
However, participating in DeFi is not without its risks, and users should exercise caution and conduct due diligence when using the platform.
Uniswap continues to evolve, with many developments and upgrades planned for the future. These include improvements to the user interface, governance enhancements, and expansion to Layer-2 scaling solutions to reduce transaction fees and increase efficiency.
How to buy UNI tokens
You can buy UNI via MoonPay or through any of our partner wallet applications with a credit card, bank transfer, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and many other payment methods.
Just enter the amount of Uniswap (UNI) you wish to purchase and follow the steps to complete your order.







