What is fiat money? A guide to fiat currency
Learn all about what fiat money is, how it functions in modern economies, and how it compares to other types of currency, both digital and physical.
By Corey Barchat
In today's global economy, the term "fiat money" frequently appears in discussions about finance and monetary systems. It's a cornerstone of modern finance, and it influences everything from daily transactions to international trade.
In the crypto community, "fiat currency" is used frequently as well to describe traditional government-issued currencies, often highlighting their perceived flaws such as centralization and inflation risks, as well as its susceptibility to government control and manipulation. In contrast, cryptocurrency hopes to offer a decentralized and deflationary alternative to traditional money.
This guide will help you understand fiat money and its role in how contemporary economies function.
What is fiat money?
Fiat money is a type of currency that a government has declared to be legal tender, but it is not backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver. Instead, its value is derived from the trust and confidence that people and institutions place in the issuing government.
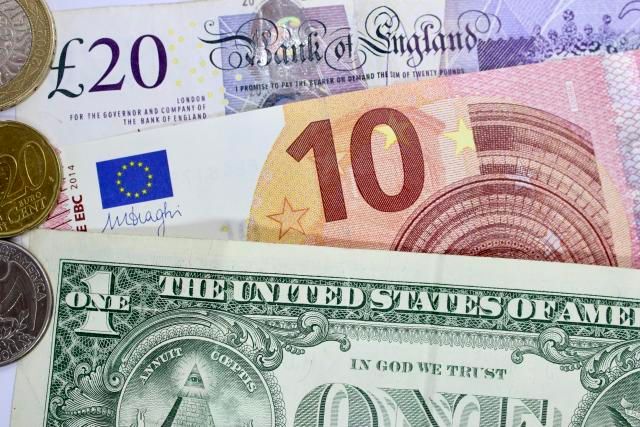

Fiat currency can function as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value within an economy. It is essential for facilitating trade, saving, and investment, and it serves as the backbone of modern economic systems.
The concept of fiat money is rooted in the authority of the government to maintain the value of the currency through regulation and economic policy. Unlike commodity money, which has intrinsic value derived from the material it is made of, fiat money’s value is symbolic, representing the trust in the economy and its governance.
How does fiat money work?
Fiat money operates based on several key principles that ensure its acceptance and stability within an economy:
Issuance
Governments and central banks play a critical role in the creation and management of fiat money. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, the European Central Bank, and the Bank of Japan, are responsible for issuing new currency.
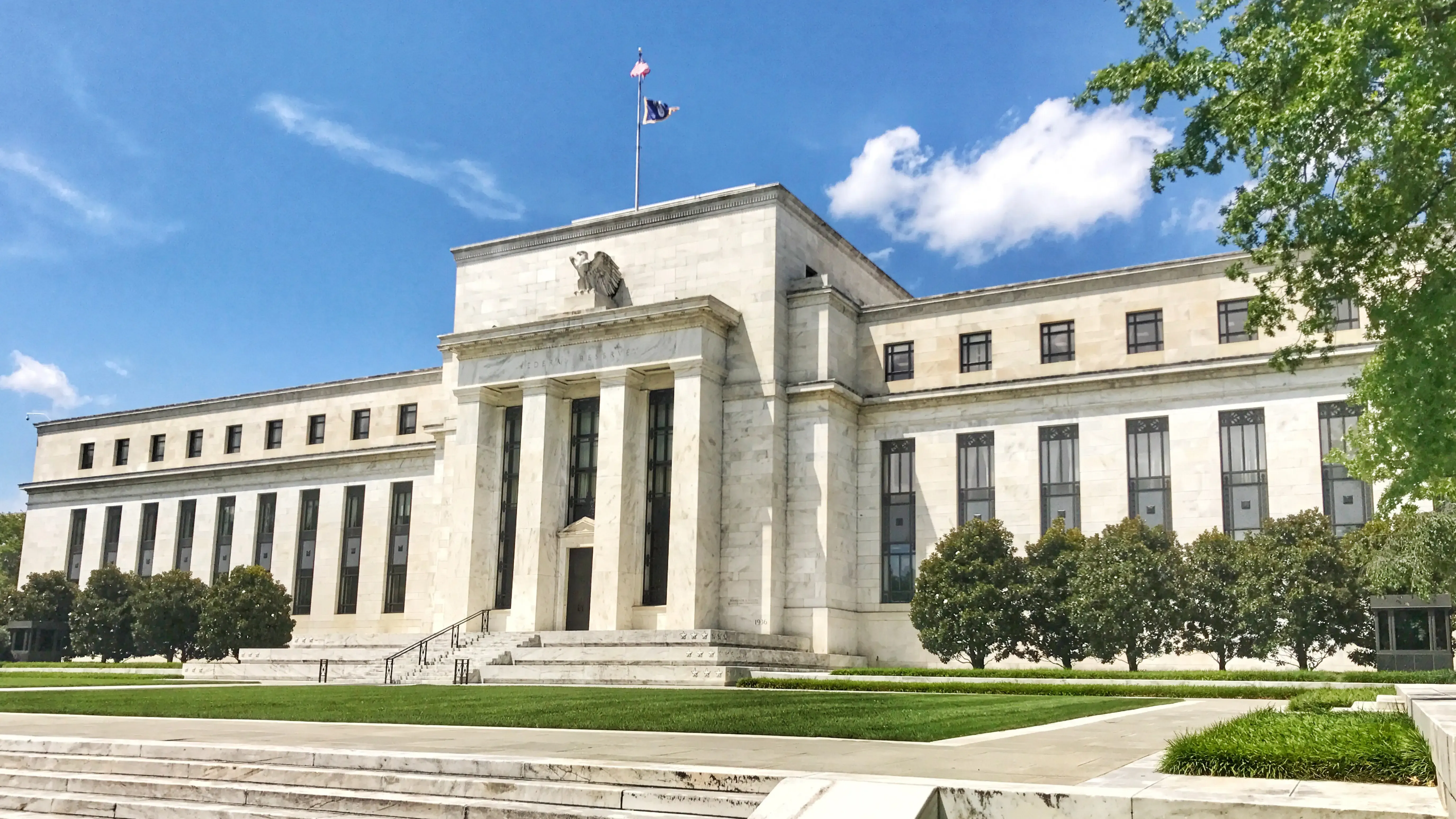

This process involves printing banknotes and minting coins (a physical version of how cryptocurrency is minted), which are then distributed through the banking system. The amount of money issued is carefully controlled to avoid excessive inflation, which can devalue the currency.
Legal tender status
Fiat money is designated as legal tender by a country's government, meaning it must be accepted as a form of payment for debts, taxes, and other financial obligations. This legal status ensures that fiat is universally accepted within the country, facilitating commerce, trade, and other financial transactions.

Legal tender laws mandate that creditors must accept fiat currency as payment, underpinning its wide acceptance and use in a particular economy. Similarly, El Salvador's decision to make Bitcoin legal tender meant that the cryptocurrency could be used in all of the same capacities as fiat currency.
Regulation and monetary policy
Regulation and monetary policy are essential for maintaining the value and stability of fiat currency. Central banks use various tools and strategies to regulate the money supply and achieve economic goals such as controlling inflation, maintaining employment levels, and promoting economic growth. Some key tools used to accomplish this include:
- Open Market Operations (OMOs): OMOs involve the buying and selling of government securities in the open market to regulate the supply of money. When a central bank buys securities, it increases the money supply; when it sells securities, it decreases the money supply.
- Interest rates: Central banks set key interest rates that influence the cost of borrowing and lending. Lowering interest rates can stimulate economic activity by making borrowing cheaper, while raising rates can help control inflation by making borrowing more expensive.
- Reserve requirements: Central banks require commercial banks to hold a certain percentage of their deposits as reserves. By adjusting these reserve requirements, central banks can influence the amount of money that banks can lend, thereby controlling the supply of money.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): This is a more unconventional monetary policy tool used in extreme economic conditions. QE involves large-scale purchases of financial assets to inject liquidity into the economy in an attempt to encourage lending and investment.
These are but a few regulatory measures and monetary policies used by central banks and governments that seek to maintain stability and trust in fiat currency. By carefully managing the supply of money and responding to economic conditions, central banks aim to prevent inflation, avoid economic recessions, and ensure that the currency remains a reliable medium of exchange and store of value.
Advantages of fiat money
Fiat currency has some key benefits over other currencies and forms of money, such as:
Economic stability and control
Fiat currency allows governments and central banks to exert significant control over the economy. As they manage the money supply and interest rate levels, they can respond to economic changes while aiming to stabilize the economy.
Flexibility in monetary policy
Fiat currency provides flexibility in monetary policy, enabling a central bank to implement measures to combat inflation, control unemployment, and stimulate economic growth. This adaptability is crucial for responding to economic crises and market fluctuations.
Ease of use and acceptance
Fiat money is widely accepted and easy to use for transactions. Its standardized units are designed to make it convenient for buying goods and services, paying taxes, and saving for the future.
Other benefits of fiat currency
Fiat currency supports the development and functioning of financial markets and institutions, facilitating investment, lending, and borrowing activities.
Limitations of fiat money
Despite its unique advantages, fiat currency also carries additional risks over other forms of currency:
Inflation and hyperinflation risks
One of the primary risks associated with fiat money is inflation. Since fiat money is not backed by a physical commodity, excessive printing of money can lead to a decrease in its value, causing inflation or even hyperinflation in extreme cases.
Dependence on government trust and stability
The value of fiat money relies heavily on the trust and stability of the particular issuing government. Political instability or loss of confidence can erode the value of fiat money, leading to economic turmoil.
Potential for mismanagement and abuse
Governments and central banks may misuse their power to issue fiat money, leading to economic problems. Mismanagement of fiat currency can result in high inflation, loss of credibility, and economic instability.
Counterfeiting
Fiat currency can be susceptible to counterfeiting, which could undermine its value and trust. While modern technologies have made counterfeiting more difficult, it remains a potential risk for physical money, as well as its digital counterpart.
Regulatory strength
Fiat money systems require robust regulatory frameworks and effective governance to function smoothly, posing challenges in regions with weaker institutions.
Fiat money vs other forms of money
While fiat monies are commonly used across the globe, they are not the only form of currency in existence:
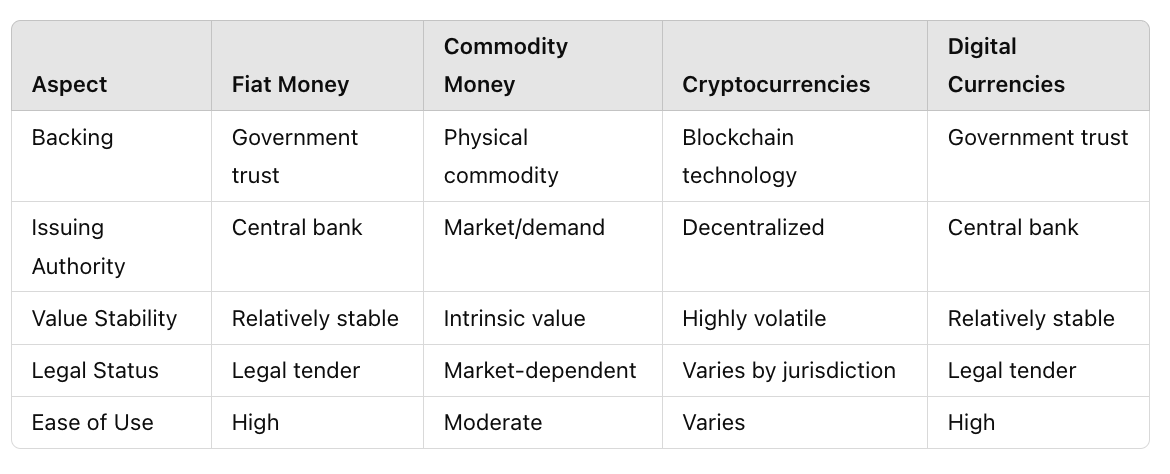
Fiat money vs. commodity money
Commodity money is backed by physical goods, such as precious metals like gold, silver, or other valuable commodities that give it intrinsic value. The value of commodity money is derived from the material itself, which means its worth is relatively stable and less prone to inflation. Historically, commodity money was used widely until the transition to fiat currencies, which offered more flexibility and efficiency in transactions and payments.
In contrast, fiat currency has no intrinsic value and is not backed by physical commodities. Its value is strictly derived from the trust and confidence in the issuing government. While this allows for greater flexibility and control, it also means that fiat money is more susceptible to inflation, and heavily relies on the stability and credibility of the government.
Fiat money vs. cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptography for security and operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology. Unlike fiat money, cryptocurrencies are not issued or controlled by any central authority, which proponents argue makes them more resistant to government interference, manipulation, and centralization.
Fiat money, on the other hand, is centrally controlled by governments and central banks. This central control allows for the implementation of monetary policies to stabilize the economy, but it also means that fiat money can be influenced by political and economic decisions.
Cryptocurrencies, with their decentralized nature, offer an alternative that is potentially less prone to inflation and political manipulation, though they come with high volatility and regulatory uncertainty.
Fiat money vs. digital currencies
Digital currencies encompass both cryptocurrencies and digital versions of fiat money. Digital fiat currencies are issued by central banks in digital form and represent a digital version of physical currency. Versions like Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCS) maintain the same value as their physical counterparts and are fully backed by the issuing authority.
Although they may appear to be similar, the main difference between digital fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies lies in their control and regulation. Digital fiat currencies are centrally controlled and regulated, similar to traditional fiat currencies, but they offer the same benefits as digital transactions, like transfer ease and enhanced security.
Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, operate independently of central banks and offer decentralized control. This can lead to greater privacy and reduced transaction costs, but it should be noted that crypto also comes with higher volatility and regulatory challenges.
Fiat money in the modern economy
The Gold Standard and its abandonment
The gold standard was a monetary system in which the value of a country's currency was tied directly to a specific amount of gold.
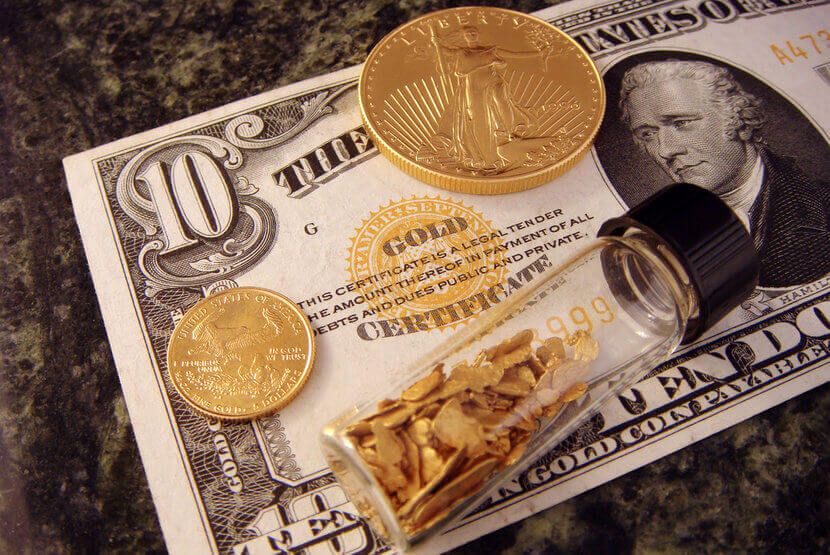

Under this standard, currencies were convertible into a fixed amount of gold, and the supply of money was limited by the amount of gold held in reserve. This system provided a high degree of currency stability and predictability, reducing inflationary pressures since the money supply could not expand arbitrarily.
However, the rigidity of the gold standard also meant that it was difficult to respond to economic crises and fluctuating demand for money. During the Great Depression, for example, countries on the gold standard struggled to implement effective monetary policies.
The system was gradually abandoned throughout the 20th century, particularly during the era of the Bretton Woods system, which ended in 1971 when the United States ceased the convertibility of the dollar into gold. This shift allowed for more flexible monetary policies, giving governments greater control over their economies.
Historical examples of fiat money
- The US Dollar: Since the United States moved away from gold, the US dollar has become the world's primary reserve currency, underpinned by the relative economic strength and stability of the United States. The Federal Reserve's monetary policy has played a key role in managing inflation and fostering economic growth, making the dollar widely trusted and accepted internationally.
- The euro: Introduced in January 1, 1999, the euro has become a major global currency, facilitating trade and economic integration among the European Union member states. The European Central Bank (ECB) manages the euro with a focus on price stability and economic growth, contributing to its success and stability.
- Zimbabwean Dollar: In the late 2000s, Zimbabwe experienced one of the most extreme cases of hyperinflation in history. Excessive printing of money by the government, in response to economic crises and fiscal mismanagement, led to hyperinflation rates reaching billions of percent, rendering the Zimbabwean dollar essentially worthless.
The future of fiat money
As technology advances, fiat money is increasingly becoming digital. While central banks and governments explore the creation of new digital currencies, others are turning to existing options like Bitcoin. In both cases, the goal is the same: to enhance the efficiency and security of transactions, and hopefully transform the financial landscape of the country for the better.
The cryptocurrency community often criticizes fiat money for its centralization and susceptibility to inflation. Advocates argue that decentralized cryptocurrencies offer a more secure and transparent alternative to traditional fiat currencies, while detractors say it is too volatile to be used as a long term store of value.
Despite the emergence of digital currencies like cryptocurrency, fiat money remains a fundamental pillar of the modern financial system. Governments around the world have shown that it can be used to promote economic stability and growth, contributing to its reputation as a widely-accepted and effective medium of exchange.
Bridging fiat currency and cryptocurrency
As the world moves further into the digital age, the role and nature of fiat money are likely to evolve, potentially incorporating digital innovations while facing competition from newer financial technologies like cryptocurrencies.
No matter which fiat currency or cryptocurrency emerges as the winner, there will always be a need to move between physical and digital currencies.
MoonPay makes it easy to convert fiat to crypto and vice versa, with support for dozens of supported fiat currencies in over 160 countries. Choose from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, and pay your way using a credit card, bank transfer, and many more payment methods.
When you decide it's time to cash out, simply sell crypto back to MoonPay and receive cash in your bank account in the fiat currency of your choice.


.png)